ResticUI with PyWebIO - Repo
Dieses Thema wurde gelöscht. Nur Nutzer mit entsprechenden Rechten können es sehen.
-
Hier mein Public Repo -> https://gitlab.com/Bullet64/restic_ui_pywebio
Im Fediverse -> @FrankM@nrw.social
- NanoPi R5S
- Quartz64 Model B, 4GB RAM
- Quartz64 Model A, 4GB RAM
- RockPro64 v2.1
-
Python - Interessante Packages
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben Python3 python linux0 Stimmen1 Beiträge160 Aufrufe -
Portfolio - mein kleines Flask Projekt
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben Python3 python flask bootstrap ki-generiert0 Stimmen5 Beiträge407 Aufrufe -
PyPi - Pakete ein Sicherheitsproblem?
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben Python3 python pypi docker0 Stimmen1 Beiträge152 Aufrufe -
Restic UI - Stand Januar 2023
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben PyWebIO restic-ui pywebio python0 Stimmen1 Beiträge171 Aufrufe -
PyWebIO - put_buttons
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben PyWebIO pywebio python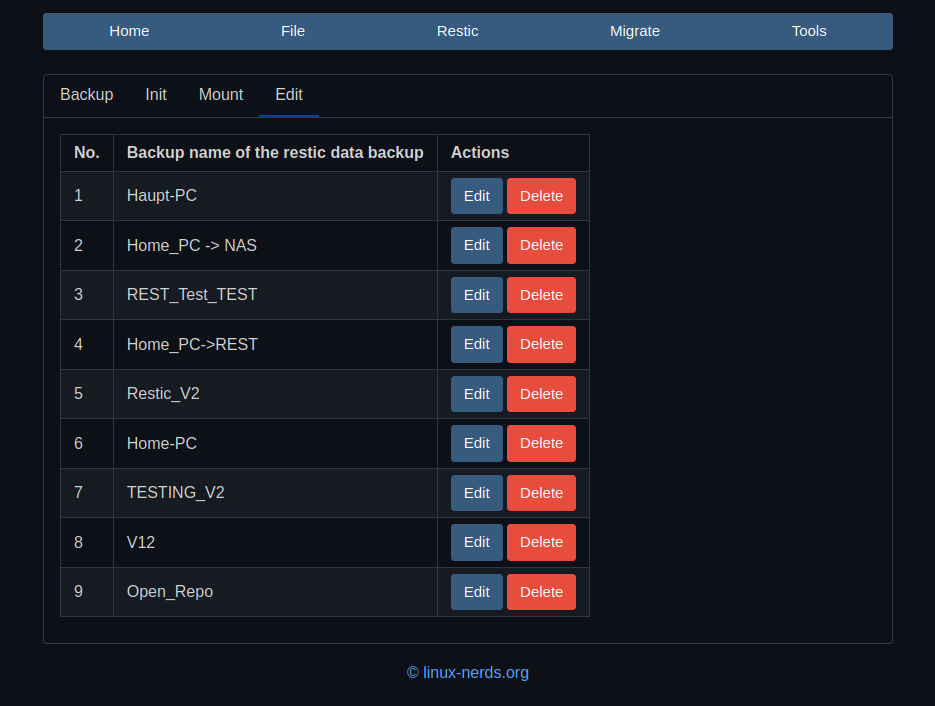 1
0 Stimmen2 Beiträge254 Aufrufe
1
0 Stimmen2 Beiträge254 Aufrufe -
Restic UI - auf PyQt6 umbauen
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben Restic UI restic-ui pyqt6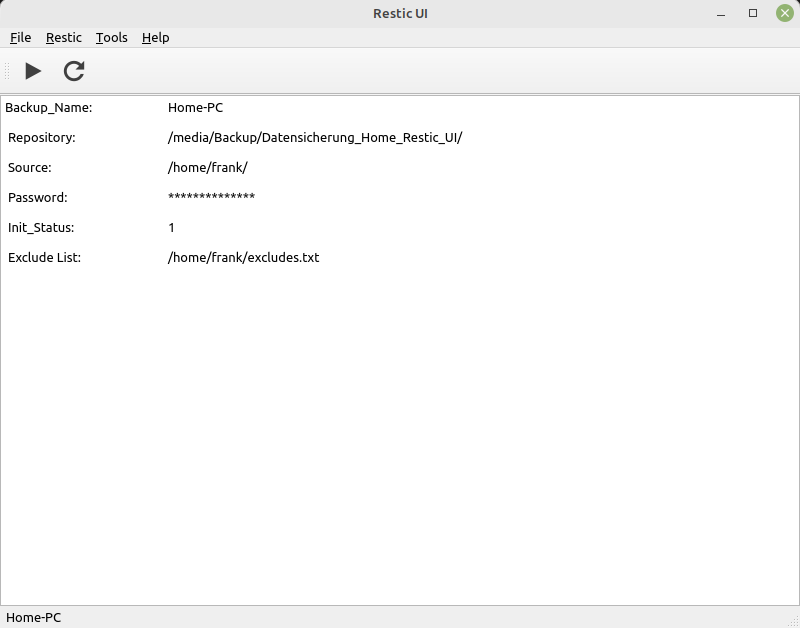 1
0 Stimmen5 Beiträge368 Aufrufe
1
0 Stimmen5 Beiträge368 Aufrufe -
PyQt6 - QSettings
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben Python3 python0 Stimmen3 Beiträge527 Aufrufe -
Restic UI - REST Server Unterstützung
Beobachtet Ignoriert Geplant Angeheftet Gesperrt Verschoben Restic UI restic-ui restic rest-server python0 Stimmen2 Beiträge328 Aufrufe