Semaphore - Die API
-
Nehmen wir mal an, wir haben bei Gitlab oder auch Github, oder was auch immer, ein Repo das wir gelegentlich bearbeiten und das danach automatisch auf einen Server soll. So was ist ja in der Entwicklung von Software normal. Dafür gibt es ganz viele Möglichkeiten, ich habe mir gedacht das kann man sicherlich auch mit einem Playbook realisieren. Mittlerweile, nach vielen Kopfschmerzen, funktioniert es.
PyCharm (commit & push) -> Gitlab -> Semaphore (Playbook) -> Server mit Applikation
Wir müssen also mit Gitlab das Playbook auf dem Semaphore Server triggern. Meine ersten Versuche zielten darauf ab, meinen lokalen Semaphore Server zu triggern. Dazu wollte ich die IPv6 Adresse benutzen. Dies scheiterte aber die ganze Zeit.
Die Docker Container, die Gitlab startet, scheinen keine IPv6 Funktionalität zu besitzen!?? Da ich aber schauen wollte, ob das so klappt wie ich mir das vorstellte, habe ich einen Semaphore Server im Netz aufgesetzt. Und da funktionierte es (IPv4 & IPv6) einwandfrei.
Ok, die Doku zur API (Application Programming Interface) findet man -> https://docs.ansible-semaphore.com/administration-guide/api
Ganz wichtig ist das Thema Authentifizierung. Damit ein User auf die API zugreifen kann, benötigt dieser meistens einen s.g. Token. Den kann man mit der API auch erzeugen, aber zuerst muss man sich mal anmelden, an der API.
LOGIN
curl -v -c /tmp/semaphore-cookie -XPOST \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Accept: application/json' \ -d '{"auth": "YOUR_LOGIN", "password": "YOUR_PASSWORD"}' \ http://localhost:3000/api/auth/loginLogin & Passowort sind die Login Daten Eures Semaphores Users. Danach ist man angemeldet und kann weiter arbeiten.
TOKEN erzeugen
curl -v -b /tmp/semaphore-cookie -XPOST \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Accept: application/json' \ http://localhost:3000/api/user/tokens curl -v -b /tmp/semaphore-cookie \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Accept: application/json' \ http://localhost:3000/api/user/tokensDanach erscheint in der Konsole die Ausgabe und man kann sich den Token kopieren. Damit kann man dann weiter arbeiten. Beispiel aus der Doku.
[{"id":"YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN","created":"2017-03-11T13:13:13Z","expired":false,"user_id":1}]Um jetzt mit Gitlab einen Task anzustoßen, braucht man diesen curl-String.
curl -v -XPOST \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Accept: application/json' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN' \ -d '{"template_id": 1}' \ http://localhost:3000/api/project/1/tasksOk, das bekommt man hin, oder? War für mich leider doch ein sehr lange Sessions des Ausprobierens usw. Das Problem war die Formatierung des curl-Strings bei gitlab. Ok, weiter geht es.
Gitlab
Wir legen im Gitlab Projekt eine Datei mit dem Namen
gitlab-ci.ymlan. Die Testdatei hat folgenden Inhalt.
# Here we test to trigger a semaphore task from gitlab runner. stages: - deploy deploy: stage: deploy script: # $SEMAPHORE_API_TOKEN is stored in gitlab Settings/ CI/CD / Variables > curl -v -XPOST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Accept: application/json' -H "Authorization: Bearer $SEMAPHORE_API_TOKEN " -d '{"template_id": 2}' https://<DOMAIN>/api/project/2/tasks only: - master # Specify the branch to trigger the pipeline (adjust as needed)Ich wollte den Code eigentlich lesbar reinschreiben, also mit \ mehrere Zeilen. Aber alle meine Versuche sind gescheitert, egal was ich im Internet gefunden habe oder auch bei ChatGPT, es ging erst als ich alles in eine Zeile geklatscht habe. Naja, dann halt nicht.
Wie ihr seht, habe ich zu dem Token was kommentiert.
# $SEMAPHORE_API_TOKEN is stored in gitlab Settings/ CI/CD / VariablesUnter dem Pfad kann man Token usw. ablegen und ihnen einen Namen geben. Damit kann man die sensiblen Informationen aus dem Code raushalten. Wenn man dann noch in den Einstellungen, den Token auf masked setzt, wird er auch in den Logs usw. nicht angezeigt, sondern maskiert.
> authorization: Bearer [MASKED]Das sieht ja schon gut aus
 Wenn man nun was in Pycharm editiert und das per commit & push nach gitlab befördert, führt gitlab nach der Ausführung der Befehle das File gitlab-ci.yml aus.
Wenn man nun was in Pycharm editiert und das per commit & push nach gitlab befördert, führt gitlab nach der Ausführung der Befehle das File gitlab-ci.yml aus.
Und das sorgt dafür, das der entsprechende Task auf dem Semaphore Server ausgeführt wird.Ein wunderbares Spielzeug
 Viel Spaß beim Spielen!
Viel Spaß beim Spielen!Wer Fehler findet, bitte kommentieren. Ich mag es nicht, wenn unnützes Zeug im Internet steht.
-
Ich hasse schlecht lesbaren Code, scheint man sich bei Python so anzugewöhnen. Habe da nochmal was mit der langen Zeile getestet.
stages: - deploy deploy: stage: deploy script: # $SEMAPHORE_API_TOKEN is stored in gitlab Settings/ CI/CD / Variables - >- curl -v XPOST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Accept: application/json' -H "Authorization: Bearer $SEMAPHORE_API_TOKEN " -d '{"template_id": 2}' https://<DOMAIN>/api/project/2/tasks only: - master # Specify the branch to trigger the pipeline (adjust as needed)Hier noch was Dr. ChatGPT dazu schreibt
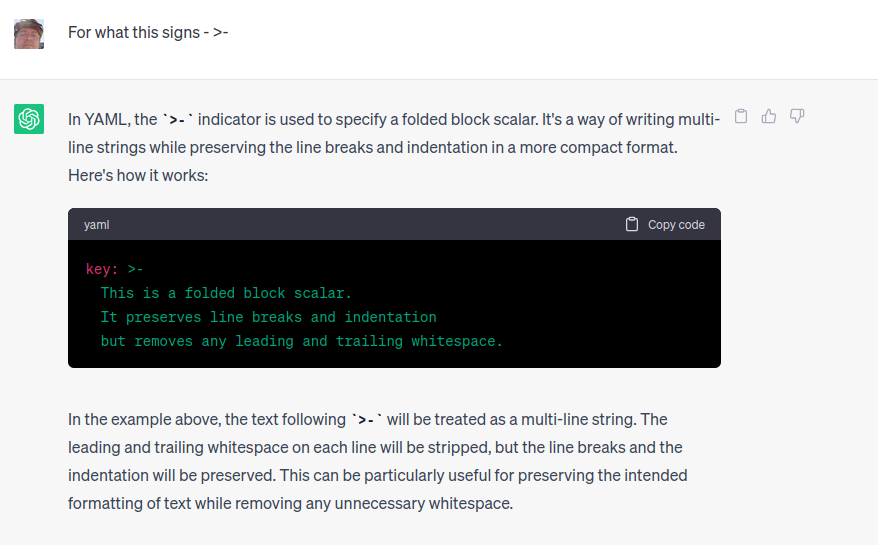
Erledigt - läuft
 Und verstanden habe ich es auch.
Und verstanden habe ich es auch. -
 F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Linux am
F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Linux am
-
-
-
-
-
-
Star64 - Warnung
Angeheftet Star64 -
-