Python - Frameworks
Python3
2
Beiträge
1
Kommentatoren
226
Aufrufe
-
Da gibt es ja sehr, sehr viel für Python. Kompliziert für Einsteiger etwas zu finden.
Der Platzhirsch Django, ist mir für einfache Dinge einfach zu viel.
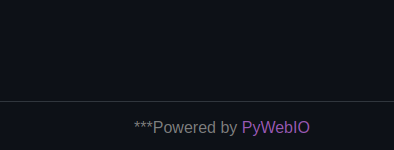
Das was ich aktuell für meine Webfrontends nutze - PyWebIO
Und hier noch zwei, wo ich drüber gestolpert bin und noch reinschauen möchte
Und es gibt noch viele mehr...
hier noch eine schöne Übersicht