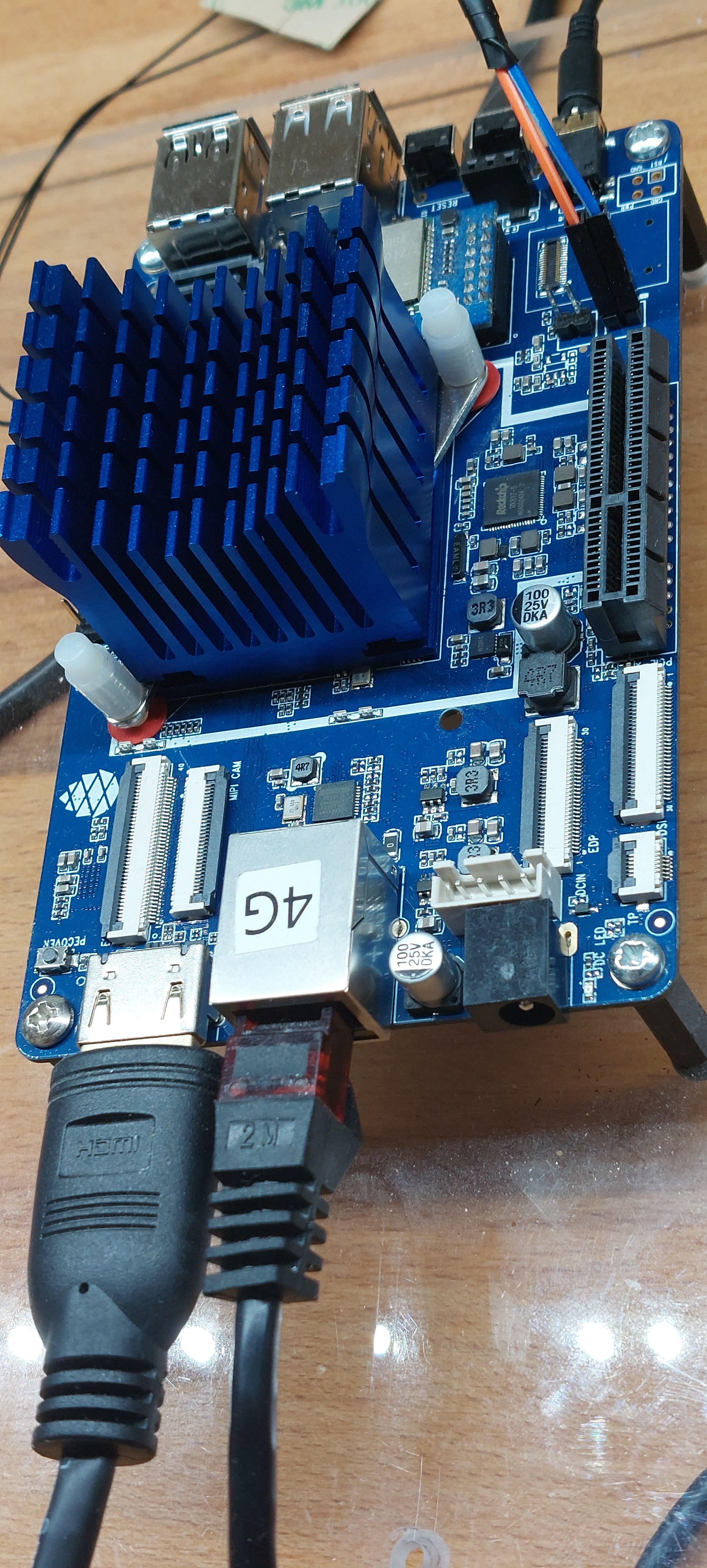
Quartz64 - Model B
-
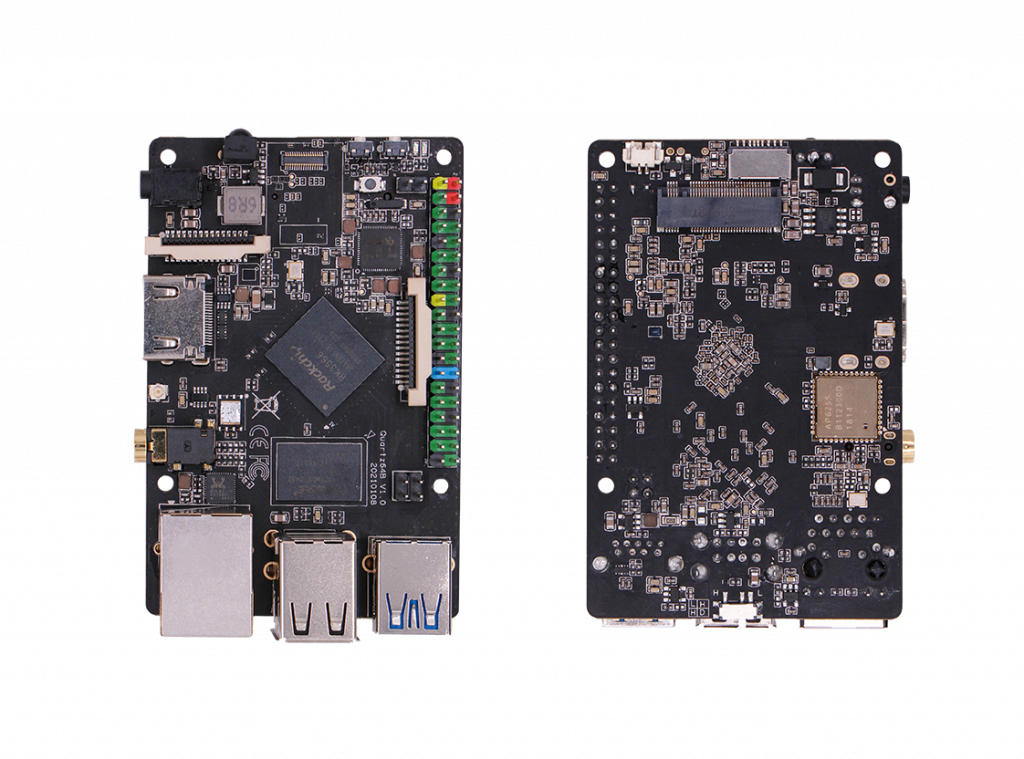
Bildquelle: https://www.pine64.org/quartz64b/5V-Stromversorgung!
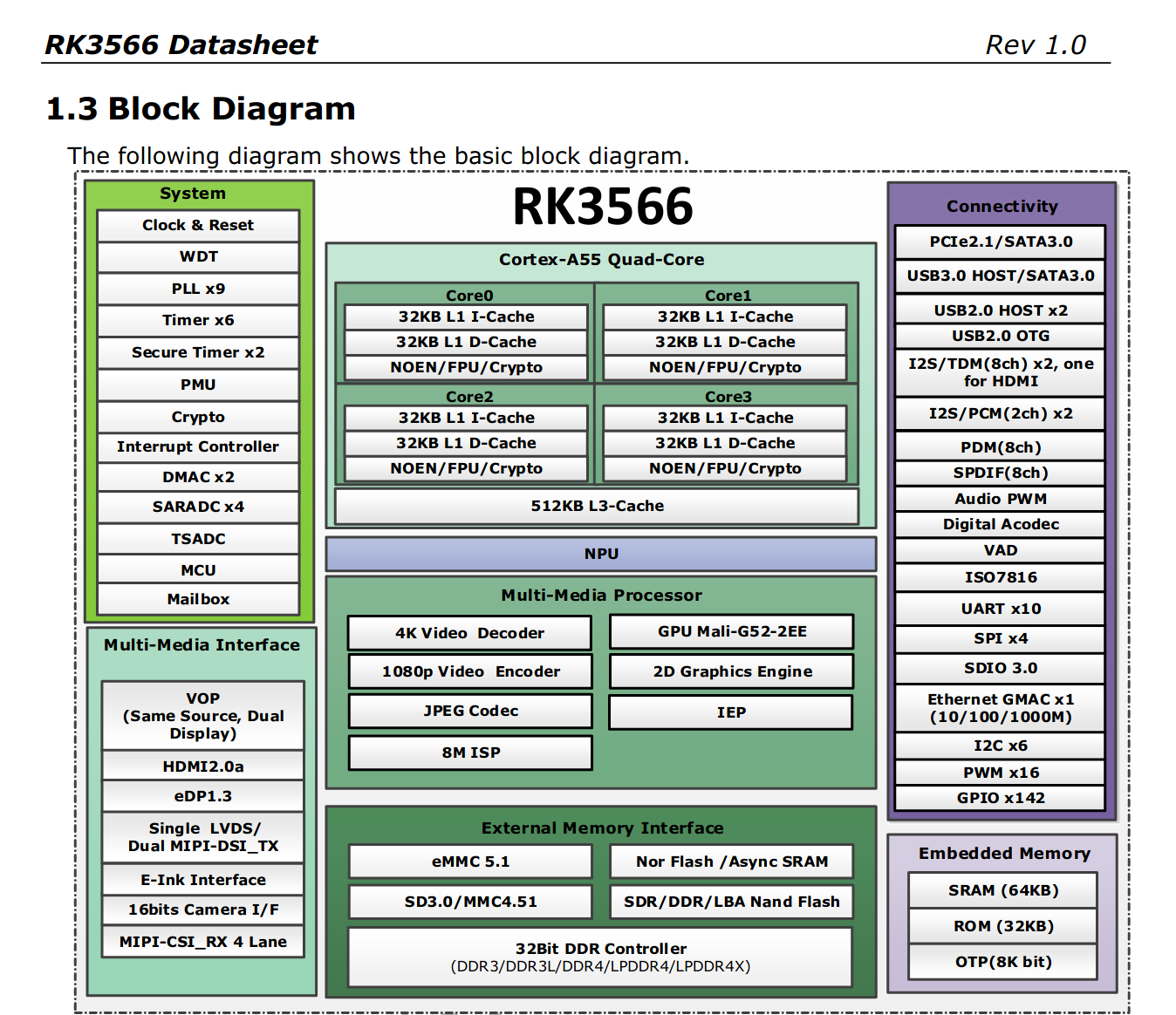
SoC and Memory Specification
- Based on Rockchip RK3566
CPU Architecture
- Quad-core ARM Cortex-A55@1.8GHz
- AArch32 for full backwards compatibility with ARMv7
- ARM Neon Advanced SIMD (single instruction, multiple data) support for accelerated media and signal processing computation
- Includes VFP hardware to support single and double-precision operations
- ARMv8 Cryptography Extensions
- Integrated 32KB L1 instruction cache and 32KB L1 data cache per core
- 512KB unified system L3 cache
- TrustZone technology support
Graphic Process Unit GPU Capability
- Mali-G52 2EE Bifrost GPU@800MHz
- 4x Multi-Sampling Anti-Aliasing (MSAA) with minimal performance drop
- 128KB L2 Cache configurations
- Supports OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0, and 3.2
- Supports Vulkan 1.0 and 1.1
- Supports OpenCL 2.0 Full Profile
- Supports 1600 Mpix/s fill rate when at 800MHz clock frequency
- Supports 38.4 GLOP/s when at 800MHz clock frequency
Neural Process Unit NPU Capability
- Neural network acceleration engine with processing performance of up to 0.8 TOPS
- Supports integer 8 and integer 16 convolution operations
- Supports the following deep learning frameworks: TensorFlow, TF-lite, Pytorch, Caffe, ONNX, MXNet, Keras, Darknet
System Memory
- RAM Memory Variants: 2GB - 8GB LPDDR4.
- SPI Flash: 128Mbit / 16MByte
Network
- 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet
- WiFi 802.11 b/g/n/ac with Bluetooth 5.0 (optional on model A, build in on model B)
Storage
- microSD - bootable, supports SDHC and SDXC, storage up to 2TB
- USB - 2 ports on model B, 3 ports on model A USB 2.0 Host port, 1 USB 3.0 Host port
- one native SATA 3.0 6Gb/s Port (only on model A, shared with USB 3.0 host port)
- optional eMMC module from 16GB up to 128GB
Expansion Ports
- eDP - 4 lanes of 2.7Gbps, up to 2560x1600@60Hz (only on model A)
- DSI - Display Serial Interface, 4 lanes MiPi, up to 1440P on model A, 2 lanes MiPi, up to 1080p on model B
- CSI - CMOS Camera Interface, 4 lanes MiPi up to 8 mega pixel on model A, 2 lanes MiPi up to 5 mega pixel on model B
- TP - Touch Panel Port, SPI with interrupt on model A
- RTC - Real Time Clock Battery Connector
- VBAT - Lithium Battery Connector with temperature sensor input on model A
- Wifi/BT Module Header - SDIO 3.0 and UART on model A, build in Wifi/BT Module on model B
- 2x20 pins "Pi2" GPIO Header on model B, 2x10 pins GPO header on model A
- PCIe x4 open ended slot on model A, m.2 slot on model B, one Gen2 lane due to SoC constraints
Quartz64 board Information, Schematics, and Certifications
-
Model "B" Baseboard Dimensions: 85mm x 56mm x 18.8mm
-
Input Power: DC 5V @ 3A 3.5mmOD/1.35mmID Barrel DC Jack connector
-
Quartz64 Model "B" SBC Schematic and PCB Board Resource:
* Quartz64 Model "B" SBC Schematic
* Quartz64 Model "B" SBC PCB Connector placement PDF file
-
-
Neuigkeiten zum WiFi-Modul, was auf dem Model B verbaut ist.
<@tl_lim> The Quartz64 model B product version will comes with BL602 module instead of AP6255.
Das macht nur 2,4 GHz

-
 F FrankM hat am auf dieses Thema verwiesen
F FrankM hat am auf dieses Thema verwiesen
-
 F FrankM hat dieses Thema am angepinnt
F FrankM hat dieses Thema am angepinnt
-
Da mein Model B ja bestellt ist, bin ich gerade über einen Post gestolpert.
<CounterPillow> "Model A" is the big form factor, "Model B" the small form factor. Model A boards generally use 12V, Model B boards use 5V.
Da sollte man also höllisch aufpassen, wenn man beide auf dem Schreibtisch liegen hat. Da ist schnell mal ein B gegrillt, wenn man das falsche Netzteil erwischt.Blödsinn! Beim Quartz64 - Modell A ist der Stecker
DC 12V @ 3A 5.5mmOD/2.1mmID center-positive Barrel DC Jack connector
beim Quartz64 - Modell B
DC 5V @ 3A 3.5mmOD/1.35mmID center-positive Barrel DC Jack connector
Passt also nicht, also alles safe

Der Schaltplan soll nächste Woche veröffentlicht werden.
CounterPillow hat mal nachgemessen
<CounterPillow> just checked with with multimeter, it is center positive
-
Quartz64 Model "B" SBC Schematic ver 1.3 20220124 PDF file veröffentlicht.
-
Manjaro Images -> https://github.com/manjaro-arm/quartz64-b-images/releases
-
Da schreibt mich das Sales Team von pine64.org an teilt mir mit, das meine PLZ falsch ist. Ja, ein scheiß Tippfehler....... Er wäre schon da

-
Er ist angekommen.
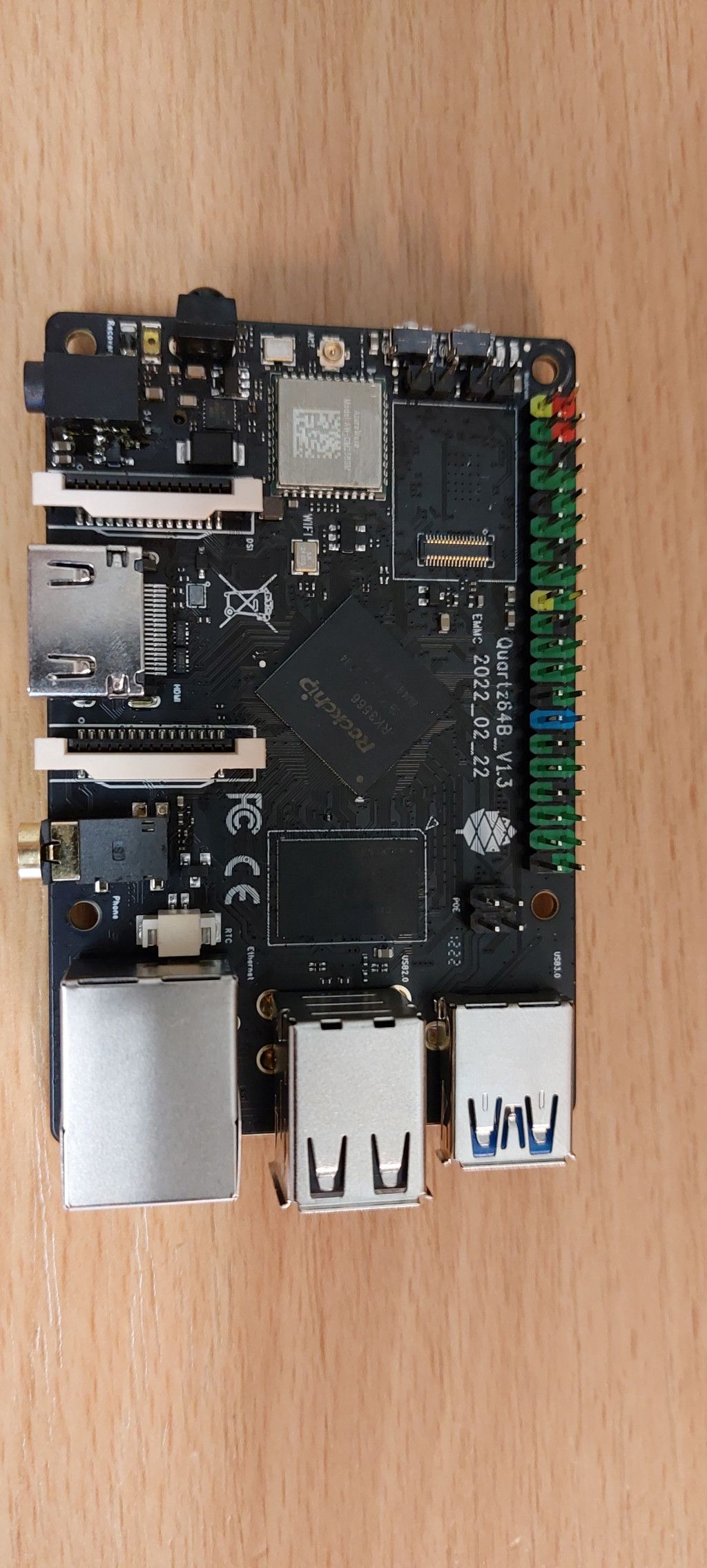
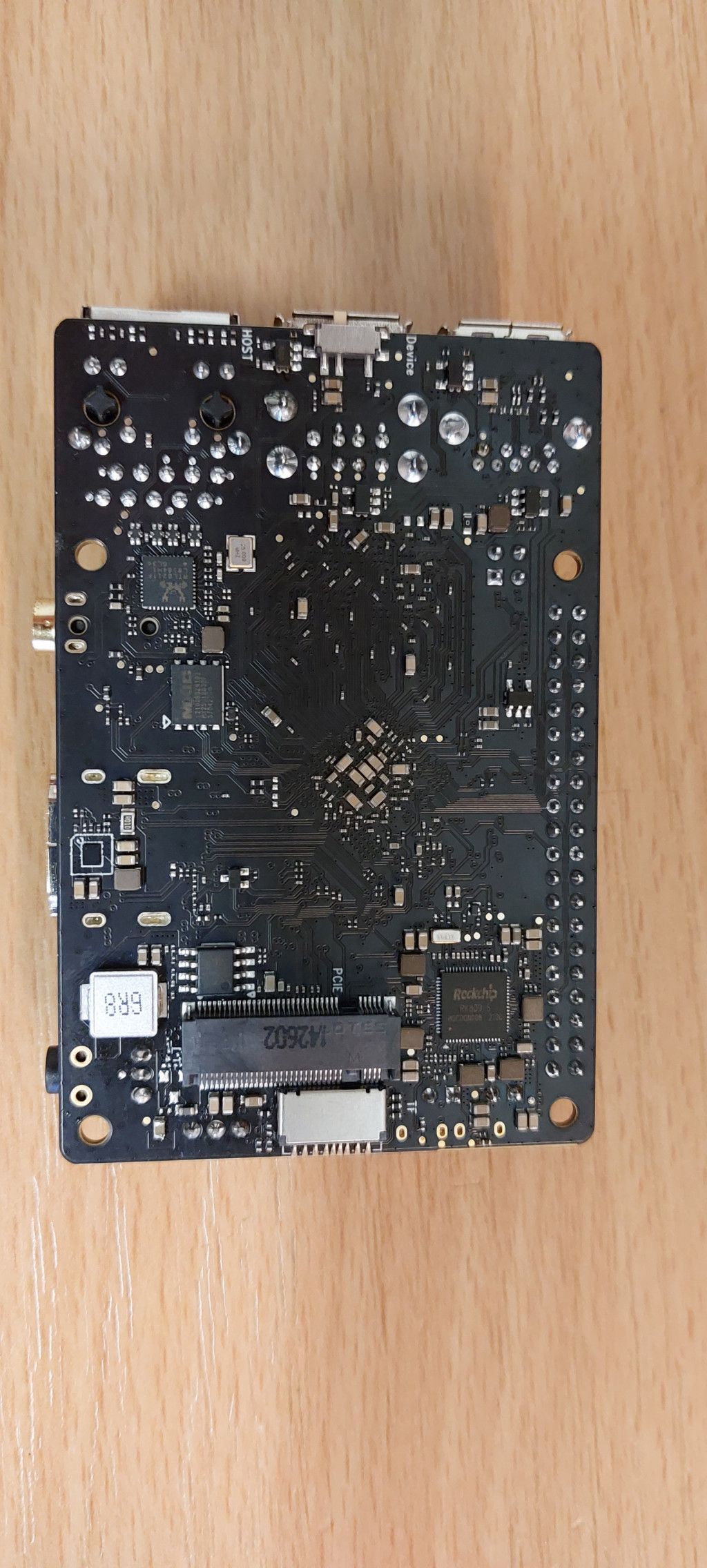


Leider funktioniert der UART Adapter nicht, jede Menge Artefakte

Ein paar Neue sind bestellt und hoffentlich morgen da. Das alte Spielkind, konnte es aber nicht lassen und musste unbedingt schauen ob der M2-Slot funktioniert.
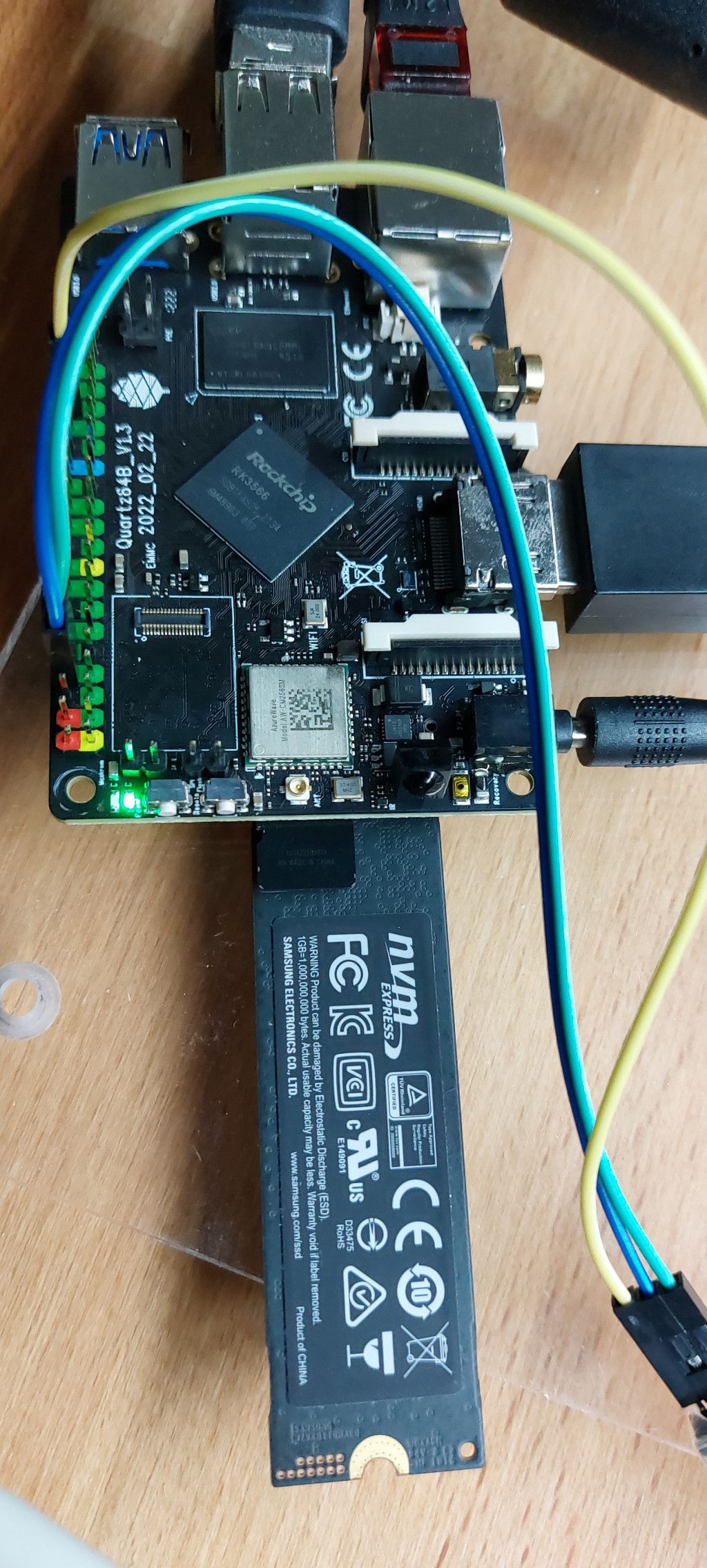

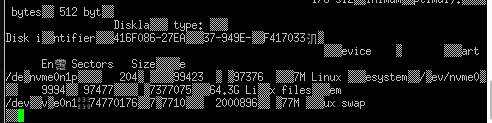
Ok, das macht natürlich NULL Spaß, also geht es morgen weiter...
-
 F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Hardware am
F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Hardware am
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Wichtige Links zum Quartz64
Angeheftet Verschoben Quartz64 -