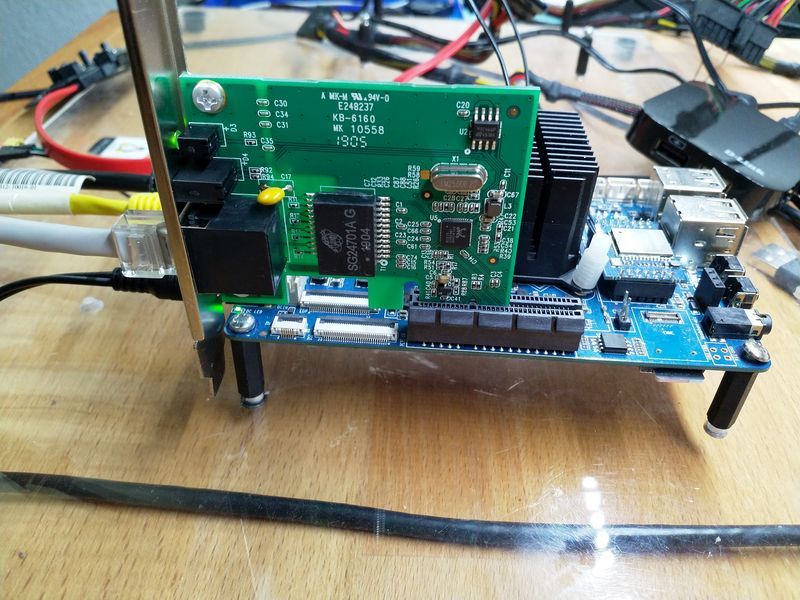
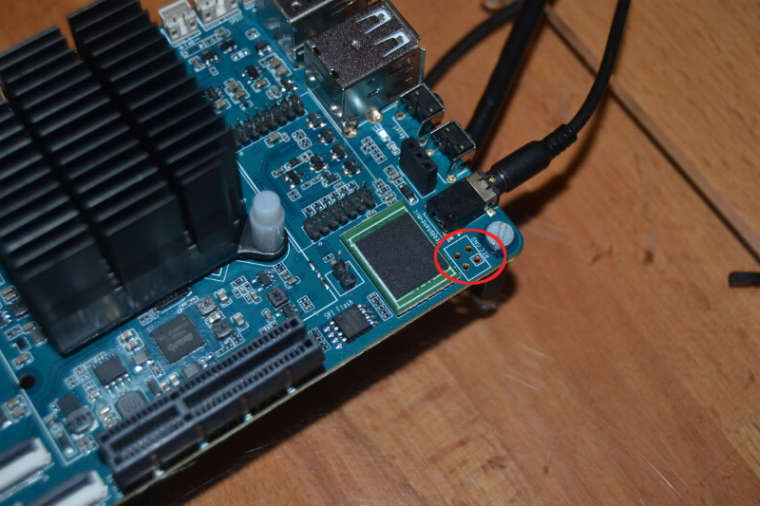
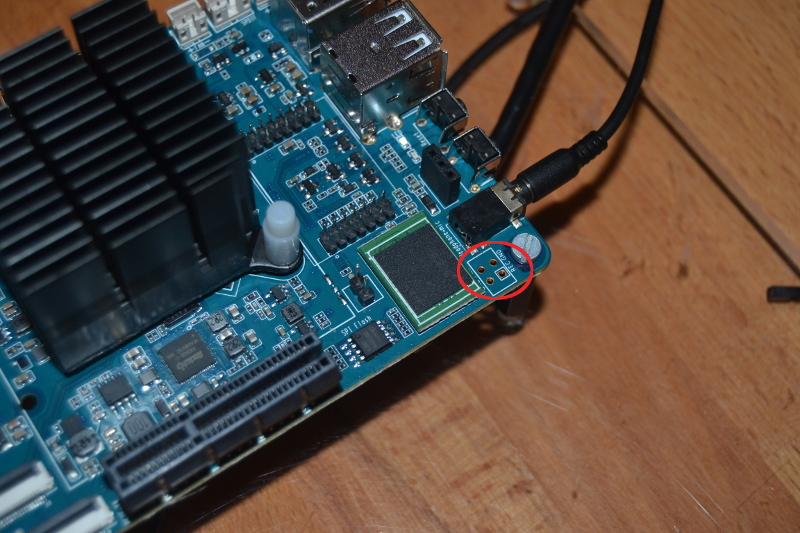
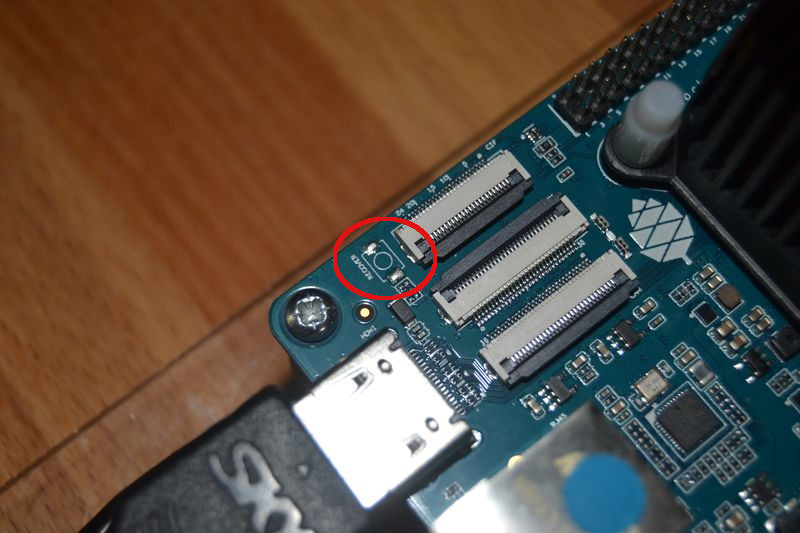
Die 970 steckt jetzt in meinem Haupt-PC. Dort werkelt ein aktuelles Linux Mint Cinnamon 19. Zum Vergleich.
100M
frank@frank-MS-7A34:~$ sudo iozone -e -I -a -s 100M -r 4k -r 16k -r 512k -r 1024k -r 16384k -i 0 -i 1 -i 2
[sudo] Passwort für frank:
Iozone: Performance Test of File I/O
Version $Revision: 3.429 $
Compiled for 64 bit mode.
Build: linux-AMD64
Contributors:William Norcott, Don Capps, Isom Crawford, Kirby Collins
Al Slater, Scott Rhine, Mike Wisner, Ken Goss
Steve Landherr, Brad Smith, Mark Kelly, Dr. Alain CYR,
Randy Dunlap, Mark Montague, Dan Million, Gavin Brebner,
Jean-Marc Zucconi, Jeff Blomberg, Benny Halevy, Dave Boone,
Erik Habbinga, Kris Strecker, Walter Wong, Joshua Root,
Fabrice Bacchella, Zhenghua Xue, Qin Li, Darren Sawyer,
Vangel Bojaxhi, Ben England, Vikentsi Lapa.
Run began: Sun Aug 19 16:52:19 2018
Include fsync in write timing
O_DIRECT feature enabled
Auto Mode
File size set to 102400 kB
Record Size 4 kB
Record Size 16 kB
Record Size 512 kB
Record Size 1024 kB
Record Size 16384 kB
Command line used: iozone -e -I -a -s 100M -r 4k -r 16k -r 512k -r 1024k -r 16384k -i 0 -i 1 -i 2
Output is in kBytes/sec
Time Resolution = 0.000001 seconds.
Processor cache size set to 1024 kBytes.
Processor cache line size set to 32 bytes.
File stride size set to 17 * record size.
random random bkwd record stride
kB reclen write rewrite read reread read write read rewrite read fwrite frewrite fread freread
102400 4 92640 121912 131074 139525 45719 116653
102400 16 254286 285267 285539 320370 108049 314486
102400 512 537947 581765 606103 598137 537701 588214
102400 1024 566892 547921 567369 597286 518014 558686
102400 16384 1407884 1642148 1941120 2115608 2006947 1668118
iozone test complete.
1000M
frank@frank-MS-7A34:~$ sudo iozone -e -I -a -s 1000M -r 4k -r 16k -r 512k -r 1024k -r 16384k -i 0 -i 1 -i 2
Iozone: Performance Test of File I/O
Version $Revision: 3.429 $
Compiled for 64 bit mode.
Build: linux-AMD64
Contributors:William Norcott, Don Capps, Isom Crawford, Kirby Collins
Al Slater, Scott Rhine, Mike Wisner, Ken Goss
Steve Landherr, Brad Smith, Mark Kelly, Dr. Alain CYR,
Randy Dunlap, Mark Montague, Dan Million, Gavin Brebner,
Jean-Marc Zucconi, Jeff Blomberg, Benny Halevy, Dave Boone,
Erik Habbinga, Kris Strecker, Walter Wong, Joshua Root,
Fabrice Bacchella, Zhenghua Xue, Qin Li, Darren Sawyer,
Vangel Bojaxhi, Ben England, Vikentsi Lapa.
Run began: Sun Aug 19 15:28:38 2018
Include fsync in write timing
O_DIRECT feature enabled
Auto Mode
File size set to 1024000 kB
Record Size 4 kB
Record Size 16 kB
Record Size 512 kB
Record Size 1024 kB
Record Size 16384 kB
Command line used: iozone -e -I -a -s 1000M -r 4k -r 16k -r 512k -r 1024k -r 16384k -i 0 -i 1 -i 2
Output is in kBytes/sec
Time Resolution = 0.000001 seconds.
Processor cache size set to 1024 kBytes.
Processor cache line size set to 32 bytes.
File stride size set to 17 * record size.
random random bkwd record stride
kB reclen write rewrite read reread read write read rewrite read fwrite frewrite fread freread
1024000 4 95635 121379 108328 108265 45369 123356
1024000 16 239238 314359 245937 241877 105865 297193
1024000 512 596812 620661 442100 382367 351948 613525
1024000 1024 608903 611898 434687 417192 412018 646465
1024000 16384 1898738 2004622 2143647 2188062 2099674 1983240
iozone test complete.
Da scheint auf dem ROCKPro64 noch ein wenig Luft nach oben.