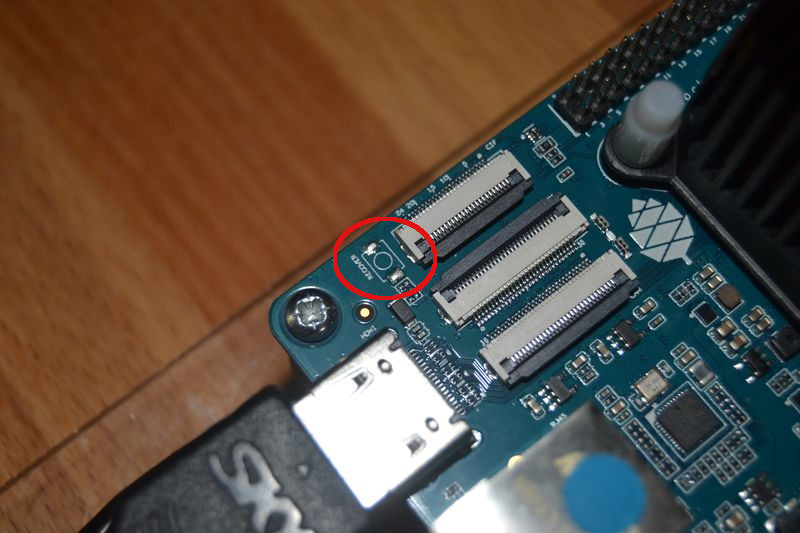
Recover Button
-
In der Version v2.0 fehlte dieser Button noch, er war einfach nicht bestückt.
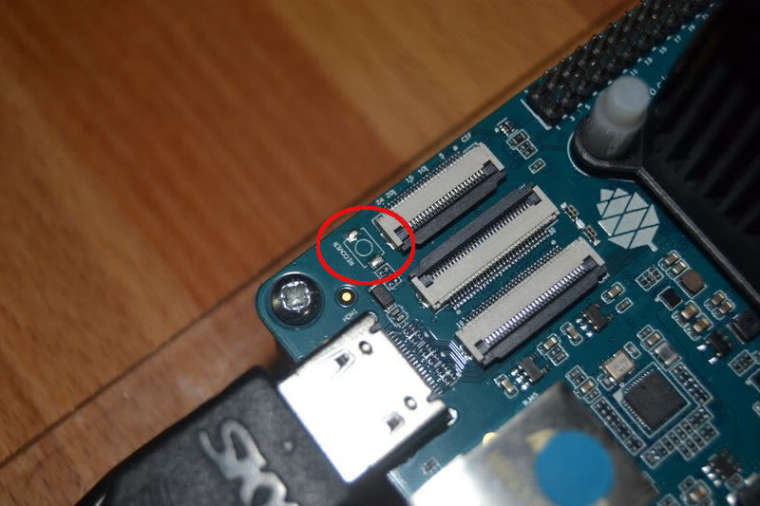
Wenn jemand den vermisst, zur Not kann man da was dran löten. Sollte machbar sein.
v2.1
Die Frage, was macht das Ding? Gehen wir mal auf die Suche.....
Kamil hat auf seiner Release Seite einen Link zu u-boot recovery selection
Kamil erklärt das so
ayufan: introduce recovery button mode selection
Press and hold recovery button to choose suitable boot mode.
When given mode is selected release the button.
Each mode exposes device over USB-OTG and can be connected via USB A-to-A cable1 blink: share eMMC or SD as virtual disk
2 blinks: enter fastboot (Android's)
3 blinks: enter RockUSB download mode
4 blinks: enter MaskROM download modeOb das so funktioniert kann ich nicht sagen, da ich nicht 100% weiß wofür das ist.
Spekulation
An die USB-C Buchse kann man ein USB A-to-A Kabel anschliessen, damit kann man dann mit verschiedenen Programmen auf das Board zugreifen.
Für Entwickler vermutlich total wichtig, denke ich das es für den durchschnittlichen Anwender unwichtig ist.
-
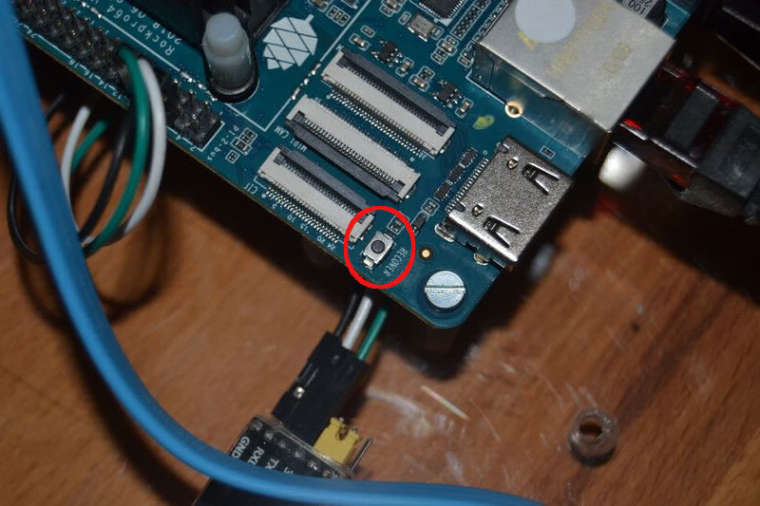
Ich hab das mal ausprobiert.
Den Recover Button so lange drücken, bis folgendes erscheint.
In: serial@ff1a0000 Out: serial@ff1a0000 Err: serial@ff1a0000 Model: Pine64 RockPro64 rockchip_dnl_mode = 1 mode rockchip_dnl_mode = 2 mode rockchip_dnl_mode = 3 mode rockchip_dnl_mode = 4 mode entering maskrom mode...RKFlashTool clonen
root@thinkpad:/home/frank/test# git clone https://github.com/rockchip-linux/rkflashtool Klone nach 'rkflashtool' ... remote: Counting objects: 663, done. remote: Total 663 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 663 Empfange Objekte: 100% (663/663), 114.94 KiB | 0 bytes/s, Fertig. Löse Unterschiede auf: 100% (367/367), Fertig.In das Verzeichnis wechseln
root@thinkpad:/home/frank/test# cd rkflashtool/Inhalt
root@thinkpad:/home/frank/test/rkflashtool# ls doc Makefile rkcrc.h rkflashtool.h rkparametersblock examples README rkflashall rkmisc rkunpack.c fixversion.sh release.sh rkflashloader rkpad rkunsign flashuboot rkcrc.c rkflashtool.c rkparameters version.hRKFlashtool bauen
root@thinkpad:/home/frank/test/rkflashtool# make gcc -O2 -W -Wall -I/usr/include/libusb-1.0 rkflashtool.c -o rkflashtool -lusb-1.0 gcc -O2 -W -Wall -I/usr/include/libusb-1.0 rkcrc.c -o rkcrc -lusb-1.0 gcc -O2 -W -Wall -I/usr/include/libusb-1.0 rkunpack.c -o rkunpack -lusb-1.0Ich habe ein USB-A to USB-A Kabel vom USB-C Port des ROCKPro64 zu meinem Notebook hergestellt.
root@thinkpad:/home/frank/test/rkflashtool# sudo ./rkflashtool v rkflashtool: info: rkflashtool v5.2 rkflashtool: info: Detected RK3399... rkflashtool: info: interface claimed rkflashtool: info: MASK ROM MODE rkflashtool: info: chip version: -..-Ok, Verbindung steht.
Eine Übersicht der Befehle
root@thinkpad:/home/frank/test/rkflashtool# sudo ./rkflashtool rkflashtool: info: rkflashtool v5.2 rkflashtool: fatal: usage: rkflashtool b [flag] reboot device rkflashtool l <file load DDR init (MASK ROM MODE) rkflashtool L <file load USB loader (MASK ROM MODE) rkflashtool v read chip version rkflashtool n read NAND flash info rkflashtool i offset nsectors >outfile read IDBlocks rkflashtool j offset nsectors <infile write IDBlocks rkflashtool m offset nbytes >outfile read SDRAM rkflashtool M offset nbytes <infile write SDRAM rkflashtool B krnl_addr parm_addr exec SDRAM rkflashtool r partname >outfile read flash partition rkflashtool w partname <infile write flash partition rkflashtool r offset nsectors >outfile read flash rkflashtool w offset nsectors <infile write flash rkflashtool p >file fetch parameters rkflashtool P <file write parameters rkflashtool e partname erase flash (fill with 0xff) rkflashtool e offset nsectors erase flash (fill with 0xff) -
 F FrankM hat am auf dieses Thema verwiesen
F FrankM hat am auf dieses Thema verwiesen