Bionic Minimal 0.7.8
-
Die aktuell letzte Version vor Kamil's wohl verdienten Urlaub

rock64@rockpro64:~$ uname -a Linux rockpro64 4.4.132-1072-rockchip-ayufan-ga1d27dba5a2e #1 SMP Sat Jul 21 20:18:03 UTC 2018 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/LinuxKamil hat das Problem mit der PCIe NVMe-Karte gefixt, aber zu Lasten das jetzt wohl kein WLan-Modul möglich ist.
(23:02:15) ayufan1: OK
(23:02:28) ayufan1: it seems that we either have sdio0 (wifi module) or pcie
(23:02:44) ayufan1: enabling sdio0 prevents the pcie from being powered
(23:02:59) ayufan1: so, either, either
(23:03:04) ayufan1: annoying
(23:03:56) fysa: that is odd
(23:04:08) fysa: same bus but switched?
(23:04:38) ayufan1: not sure, like removing the resistor on 2.0 board is not enough
(23:04:42) ayufan1: it is still being pulled
(23:10:27) ayufan1: another possibility is a mess with clocks
(23:10:47) ayufan1: anyway, disabling sdio0 makes it work stable
Eine etwas größere Baustelle!? Ich bin kein Experte, warten wir es ab. Ich persönlich habe zwar ein WLan-Modul bestellt - zum Testen - benötige WLan aber nicht für meine Platinen. Bin kein Freund von WLan.
Das Rebooten des ROCKPro64 funktioniert jetzt endlich einwandfrei! Yeah! Somit kann man langsam mal an das Bauen eines Systemes denken...
Wir haben zwei Button auf dem Board, einmal Reset, einmal Power.
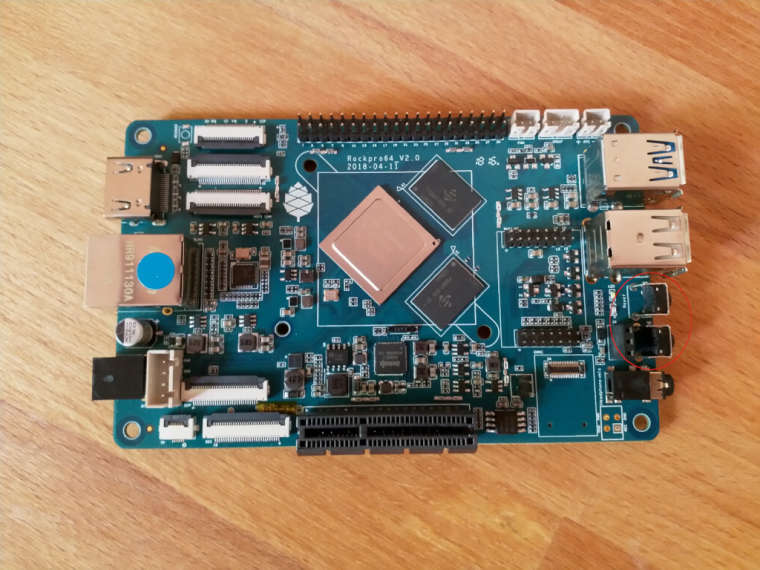
Der obere ist der Reset Button, der da drunter der Power Button. Der Reset Button ist klar, der macht einen Reset und der ROCKPro64 startet neu. Was macht der Power Button? Denkt an Euer Smartphone, wenn man dort den Bildschirm ausmacht "schläft" das Ding ein. Suspend Mode. Genau das macht dieser Button. Bei einem Druck auf den Button geht der ROCKPro64 in den Suspend Modus.
In diesem Modus benötigt er ca. 1,4 Watt, also ca. 1/4 vom normalen Verbrauch.
Diesen Suspend Mode gibt es übrigens im Mainline nicht, weil dort wohl kein Suspend Modul vorhanden ist.
https://github.com/ayufan-rock64/linux-build/issues/245Zum Aufwachen muss man etwas länger auf den Button drücken. Dann erwacht das System wieder.
Eine vorhandene USB3-SSD wird auch nach dem Start automatisch erkannt, ich hatte da vorher Probleme mit. Das kann aber auch an den grottenschlechten Adaptern liegen. Ich habe hier drei Stück, die wohl alle nicht der Hit sind.
Bei meiner nächsten Lieferung, soll am Mittwoch 25. Juli hier sein, kommt ein USB3 Adapter mit. Der soll ordentlich funktionieren, ich bin sehr gespannt.
https://www.pine64.org/?product=usb-3-0-to-sata-iii-hard-drive-adapter-cable-converter-with-uaspWer bis jetzt gezögert hat sich einen zu bestellen, das könnt ihr ohne großes Risiko machen. Die Version arbeitet, und zwar sehr stabil. Natürlich gibt es an dem Image noch jede Menge zu optimieren, aber erst mal haben wir was zum Spielen