ROCKPro64 - Armbian - Go & Restic installieren!
-
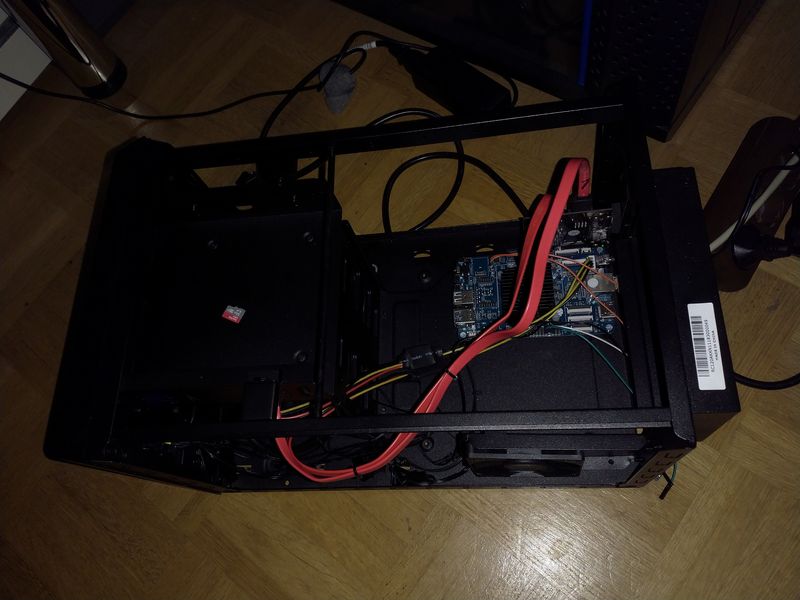
Da ich ja heute ziemlich gescheitert bin, Go und Restic zu installieren, hier mal ein neuer Ansatz. Ich will ja immer noch die USB3 HDD in mein NAS einbauen

Go installieren
Das File holen, ich hatte natürlich vorher das Falsche installiert
 Naja, macht nix. Hier das Richtige für den ROCKPro64 mit Armbian.
Naja, macht nix. Hier das Richtige für den ROCKPro64 mit Armbian.wget https://dl.google.com/go/go1.11.4.linux-arm64.tar.gzDas File dann auspacken nach /usr/local
tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.11.4.linux-arm64.tar.gzDanach im Profil den Suchpfad für das Programm einbauen.
nano /etc/profileGanz ans Ende folgendes einfügen.
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/binDanach funktioniert die Programmiersprache Go wie gewünscht.
root@rockpro64:~# go version go version go1.11.4 linux/arm64Restic
Das File bei guthub abholen.
root@rockpro64:/home/frank# git clone https://github.com/restic/restic Cloning into 'restic'... remote: Enumerating objects: 6, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (6/6), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (6/6), done. remote: Total 49414 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 49408 Receiving objects: 100% (49414/49414), 54.98 MiB | 7.39 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (30365/30365), done.Ins Verzeichnis wechseln.
root@rockpro64:/home/frank# cd restic/Restic bauen
root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic# go run build.go go: finding github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap v1.0.0 go: finding github.com/pkg/xattr v0.3.1 go: finding github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go v3.2.0+incompatible go: finding github.com/russross/blackfriday v1.5.1 go: finding github.com/satori/go.uuid v1.2.0 go: finding github.com/spf13/cobra v0.0.3 go: finding github.com/dnaeon/go-vcr v0.0.0-20180814043457-aafff18a5cc2 go: finding github.com/pmezard/go-difflib v1.0.0 go: finding cloud.google.com/go v0.27.0 go: finding gopkg.in/ini.v1 v1.38.2 go: finding github.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-go v20.1.0+incompatible go: finding golang.org/x/oauth2 v0.0.0-20180821212333-d2e6202438be go: finding github.com/elithrar/simple-scrypt v1.3.0 go: finding github.com/mattn/go-isatty v0.0.4 go: finding golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20180906233101-161cd47e91fd go: finding gopkg.in/yaml.v2 v2.2.1 go: finding google.golang.org/appengine v1.1.0 go: finding github.com/google/go-cmp v0.2.0 go: finding gopkg.in/tomb.v2 v2.0.0-20161208151619-d5d1b5820637 go: finding github.com/pkg/profile v1.2.1 go: finding gopkg.in/check.v1 v1.0.0-20180628173108-788fd7840127 go: finding google.golang.org/api v0.0.0-20180907210053-b609d5e6b7ab go: finding golang.org/x/text v0.3.0 go: finding github.com/pkg/sftp v1.8.2 go: finding github.com/minio/minio-go v6.0.7+incompatible go: finding github.com/restic/chunker v0.2.0 go: finding github.com/kr/pretty v0.1.0 go: finding github.com/jtolds/gls v4.2.1+incompatible go: finding gopkg.in/check.v1 v0.0.0-20161208181325-20d25e280405 go: finding github.com/gopherjs/gopherjs v0.0.0-20180825215210-0210a2f0f73c go: finding github.com/go-ini/ini v1.38.2 go: finding github.com/cpuguy83/go-md2man v1.0.8 go: finding github.com/golang/protobuf v1.2.0 go: finding golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20180525142821-c11f84a56e43 go: finding github.com/pkg/errors v0.8.0 go: finding golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20180907202204-917fdcba135d go: finding github.com/smartystreets/goconvey v0.0.0-20180222194500-ef6db91d284a go: finding github.com/kurin/blazer v0.5.1 go: finding github.com/stretchr/testify v1.2.2 go: finding github.com/mitchellh/go-homedir v1.0.0 go: finding golang.org/x/crypto v0.0.0-20180904163835-0709b304e793 go: finding github.com/cenkalti/backoff v2.0.0+incompatible go: finding github.com/Azure/go-autorest v10.15.3+incompatible go: finding github.com/ncw/swift v1.0.41 go: finding github.com/juju/ratelimit v1.0.1 go: finding github.com/kr/fs v0.1.0 go: finding github.com/smartystreets/assertions v0.0.0-20180820201707-7c9eb446e3cf go: finding github.com/davecgh/go-spew v1.1.1 go: finding github.com/kr/text v0.1.0 go: finding github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru v0.5.0 go: finding github.com/spf13/pflag v1.0.2 go: finding github.com/marstr/guid v1.1.0 go: finding golang.org/x/sync v0.0.0-20180314180146-1d60e4601c6f go: finding github.com/kr/pty v1.1.1 go: finding bazil.org/fuse v0.0.0-20180421153158-65cc252bf669 root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic#Fertig! Restic läuft?
root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic# ./restic restic is a backup program which allows saving multiple revisions of files and directories in an encrypted repository stored on different backends. Usage: restic [command] Available Commands: backup Create a new backup of files and/or directories cache Operate on local cache directories cat Print internal objects to stdout check Check the repository for errors diff Show differences between two snapshots dump Print a backed-up file to stdout find Find a file, a directory or restic IDs forget Remove snapshots from the repository generate Generate manual pages and auto-completion files (bash, zsh) help Help about any command init Initialize a new repository key Manage keys (passwords) list List objects in the repository ls List files in a snapshot migrate Apply migrations mount Mount the repository prune Remove unneeded data from the repository rebuild-index Build a new index file recover Recover data from the repository restore Extract the data from a snapshot self-update Update the restic binary snapshots List all snapshots stats Scan the repository and show basic statistics tag Modify tags on snapshots unlock Remove locks other processes created version Print version information Flags: --cacert file file to load root certificates from (default: use system certificates) --cache-dir string set the cache directory. (default: use system default cache directory) --cleanup-cache auto remove old cache directories -h, --help help for restic --json set output mode to JSON for commands that support it --key-hint string key ID of key to try decrypting first (default: $RESTIC_KEY_HINT) --limit-download int limits downloads to a maximum rate in KiB/s. (default: unlimited) --limit-upload int limits uploads to a maximum rate in KiB/s. (default: unlimited) --no-cache do not use a local cache --no-lock do not lock the repo, this allows some operations on read-only repos -o, --option key=value set extended option (key=value, can be specified multiple times) -p, --password-file string read the repository password from a file (default: $RESTIC_PASSWORD_FILE) -q, --quiet do not output comprehensive progress report -r, --repo string repository to backup to or restore from (default: $RESTIC_REPOSITORY) --tls-client-cert string path to a file containing PEM encoded TLS client certificate and private key -v, --verbose n be verbose (specify --verbose multiple times or level n) Use "restic [command] --help" for more information about a command. root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic# ./restic version restic 0.9.3 (v0.9.3-83-g0dd80542) compiled with go1.11.4 on linux/arm64Damit wir das aber an der richtigen Stelle haben, kopieren wir das mal nach /usr/bin
root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic# sudo cp restic /usr/binNun kann man das Programm von überall aufrufen.
root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic# restic restic is a backup program which allows saving multiple revisions of files and directories in an encrypted repository stored on different backends. Usage: restic [command] Available Commands: backup Create a new backup of files and/or directories cache Operate on local cache directories cat Print internal objects to stdout check Check the repository for errors diff Show differences between two snapshots dump Print a backed-up file to stdout find Find a file, a directory or restic IDs forget Remove snapshots from the repository generate Generate manual pages and auto-completion files (bash, zsh) help Help about any command init Initialize a new repository key Manage keys (passwords) list List objects in the repository ls List files in a snapshot migrate Apply migrations mount Mount the repository prune Remove unneeded data from the repository rebuild-index Build a new index file recover Recover data from the repository restore Extract the data from a snapshot self-update Update the restic binary snapshots List all snapshots stats Scan the repository and show basic statistics tag Modify tags on snapshots unlock Remove locks other processes created version Print version information Flags: --cacert file file to load root certificates from (default: use system certificates) --cache-dir string set the cache directory. (default: use system default cache directory) --cleanup-cache auto remove old cache directories -h, --help help for restic --json set output mode to JSON for commands that support it --key-hint string key ID of key to try decrypting first (default: $RESTIC_KEY_HINT) --limit-download int limits downloads to a maximum rate in KiB/s. (default: unlimited) --limit-upload int limits uploads to a maximum rate in KiB/s. (default: unlimited) --no-cache do not use a local cache --no-lock do not lock the repo, this allows some operations on read-only repos -o, --option key=value set extended option (key=value, can be specified multiple times) -p, --password-file string read the repository password from a file (default: $RESTIC_PASSWORD_FILE) -q, --quiet do not output comprehensive progress report -r, --repo string repository to backup to or restore from (default: $RESTIC_REPOSITORY) --tls-client-cert string path to a file containing PEM encoded TLS client certificate and private key -v, --verbose n be verbose (specify --verbose multiple times or level n) Use "restic [command] --help" for more information about a command. root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic# restic version restic 0.9.3 (v0.9.3-83-g0dd80542) compiled with go1.11.4 on linux/arm64 root@rockpro64:/home/frank/restic#Wenn sich jemand fragt, warum man das selber baut und damit natürlich ein wenig Arbeit hat. Das Restic was in den normalen Quellen ist, ist viel zu alt. Kann ich nicht gebrauchen.
Wieder ein Schritt weiter!!
 Jetzt kann ich ja das NAS wieder in Angriff nehmen!
Jetzt kann ich ja das NAS wieder in Angriff nehmen!