Qt 5 Designer
-
ich habe die Tage mal den Qt 5 Designer ausprobiert.
Installation
apt://qttools5-dev-toolsUnd da ich hier das erste Mal auf apt:// gestoßen bin, habe ich mal nachgesehen, was das ist.
apturl ist eine kleine Ergänzung für Firefox, Epiphany und apt-get, das die Installation von Paketen über die Adresszeile des Browsers bzw. durch einen simplen Linksklick linke Maustaste erlaubt. Mit einem kleinen manuellen Eingriff kann man apturl auch mit anderen Browsern nutzen.
Wenn man auf so einen Link klickt, kommt folgendes Fenster im FF
Damit kann man dann den Designer installieren.
Test Programm
Mein kleines Testprogramm, was nichts anderes macht, als das UI zu laden und anzuzeigen.
from PyQt6 import QtWidgets, uic import sys class Ui(QtWidgets.QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super(Ui, self).__init__() # Call the inherited classes __init__ method uic.loadUi('test.ui', self) # Load the .ui file self.show() # Show the GUI app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv) # Create an instance of QtWidgets.QApplication window = Ui() # Create an instance of our class app.exec() # Start the applicationDas UI sieht so aus test.ui
GNU nano 4.8 test.ui <string>Restic UI</string> </property> <widget class="QWidget" name="centralwidget"> <widget class="QListView" name="listView"> <property name="geometry"> <rect> <x>0</x> <y>0</y> <width>1131</width> <height>551</height> </rect> </property> </widget> <widget class="QWidget" name="horizontalLayoutWidget"> <property name="geometry"> <rect> <x>0</x> <y>0</y> <width>1131</width> <height>541</height> </rect> </property> <layout class="QHBoxLayout" name="horizontalLayout"> <property name="sizeConstraint"> <enum>QLayout::SetDefaultConstraint</enum> </property> </layout> </widget> <zorder>horizontalLayoutWidget</zorder> <zorder>listView</zorder> </widget> <widget class="QMenuBar" name="menubar"> <property name="geometry"> <rect> <x>0</x> <y>0</y> <width>1125</width> <height>21</height> </rect> </property> <widget class="QMenu" name="menuTest"> <property name="title"> <string>File</string> </property> <addaction name="actionLoad_File"/> <addaction name="actionAdd_Backup"/> <addaction name="actionEdit_Backup"/> <addaction name="actionDelete_Backup"/> </widget> <addaction name="menuTest"/> </widget> <widget class="QStatusBar" name="statusbar"/> <action name="actionLoad_File"> <property name="text"> <string>Load File</string> </property> </action> <action name="actionAdd_Backup"> <property name="text"> <string>Add Backup</string> </property> </action> <action name="actionEdit_Backup"> <property name="text"> <string>Edit Backup</string> </property> </action> <action name="actionDelete_Backup"> <property name="text"> <string>Delete Backup</string> </property> </action> </widget> <resources/> <connections/> </ui>Das gestartete Programm sieht so aus
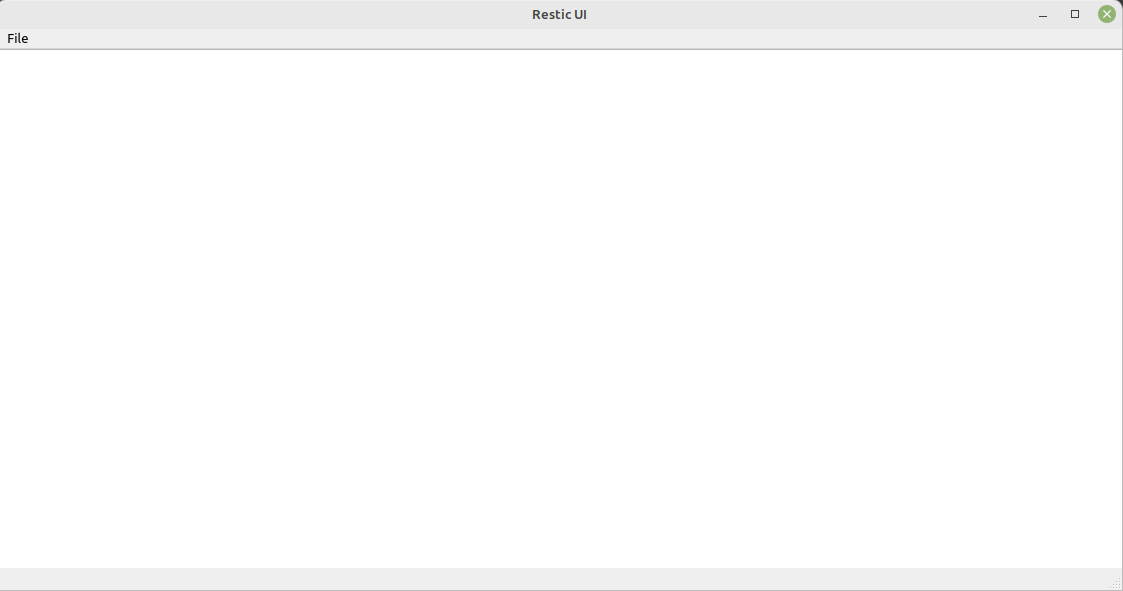
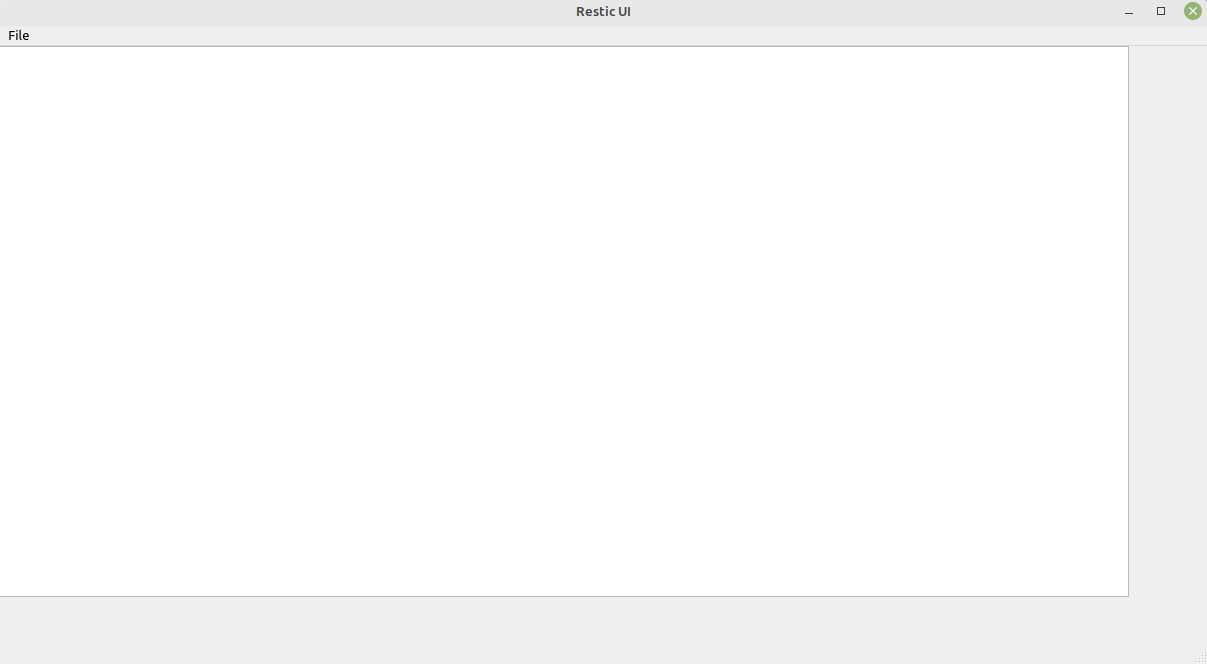
Was mich bei einem kurzen Test etwas verwirrt hat ist, das UI ist nicht responsiv. In dem Beispiel ist ein List View. Wenn ich das Fenster größer ziehe, bleibt die Größe des List View fix. In meinem Restic UI, erstellt mit PyQt6, ändert sich das so wie man es erwartet. Ich habe vermutlich nicht das Konzept dahinter verstanden, kommt aber noch - hoffe ich.
-
-
-
Python & Redis-Datenbank
Verschoben Linux -
-
-
-
-