Proxmox - Neue HDD hinzufügen
-
Proxmox macht vieles wie Linux, aber nicht alles. Aber, es hat ein sehr gutes Konzept und eine sehr gute Anleitung.
Nehmen wir an, wir hätten eine neue HDD und wollen diese für unseren Proxmox nutzen. Am Anfang muss man sich ganz schön Gedanken machen, wie man die Festplatten usw. nutzt. Mein aktueller Stand vor dem Einbau.
- SSD 240GB Betriebssystem
- NVMe SSD 500GB für die VM's
Meine aktuelle Struktur sieht so aus
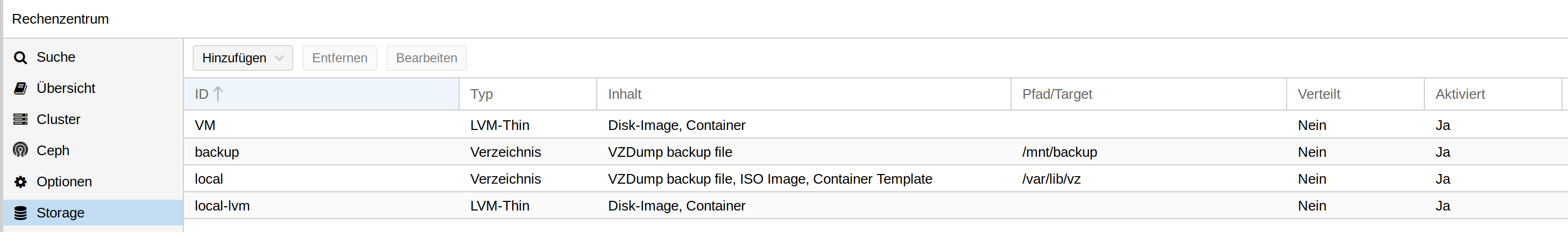
root@frank-mankel:~# pvesm status Name Type Status Total Used Available % VM lvmthin active 488136704 23284120 464852583 4.77% local dir active 57278576 3119556 51219732 5.45% local-lvm lvmthin active 147275776 0 147275776 0.00%Mit fdsik -l sehen wir nach dem Einbau folgendes
Disk /dev/sdb: 3.7 TiB, 4000787030016 bytes, 7814037168 sectors Disk model: WDC WD40EZRZ-00G Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytesMein Plan ist es, die Platte in zwei Partitionen zu unterteilen.
root@frank-mankel:~# gdisk GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 1.0.3 Type device filename, or press <Enter> to exit: /dev/sdb Partition table scan: MBR: not present BSD: not present APM: not present GPT: not present Creating new GPT entries. Command (? for help): n Partition number (1-128, default 1): First sector (34-7814037134, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: Last sector (2048-7814037134, default = 7814037134) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: 3907018567 Current type is 'Linux filesystem' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem' Command (? for help): n Partition number (2-128, default 2): First sector (34-7814037134, default = 3907018752) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: Last sector (3907018752-7814037134, default = 7814037134) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: Current type is 'Linux filesystem' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem' Command (? for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 7814037168 sectors, 3.6 TiB Model: WDC WD40EZRZ-00G Sector size (logical/physical): 512/4096 bytes Disk identifier (GUID): E625BB03-8BE4-49B4-9089-78D236650F3E Partition table holds up to 128 entries Main partition table begins at sector 2 and ends at sector 33 First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 7814037134 Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries Total free space is 2198 sectors (1.1 MiB) Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name 1 2048 3907018567 1.8 TiB 8300 Linux filesystem 2 3907018752 7814037134 1.8 TiB 8300 Linux filesystem Command (? for help): w Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING PARTITIONS!! Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): Y OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdb. The operation has completed successfully.Nun haben wir zwei Partitionen.
Disk /dev/sdb: 3.7 TiB, 4000787030016 bytes, 7814037168 sectors Disk model: WDC WD40EZRZ-00G Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disklabel type: gpt Disk identifier: E625BB03-8BE4-49B4-9089-78D236650F3E Device Start End Sectors Size Type /dev/sdb1 2048 3907018567 3907016520 1.8T Linux filesystem /dev/sdb2 3907018752 7814037134 3907018383 1.8T Linux filesystemPartition 1 formatieren
root@frank-mankel:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 mke2fs 1.44.5 (15-Dec-2018) Creating filesystem with 488377065 4k blocks and 122101760 inodes Filesystem UUID: a9a466bb-61db-4500-8027-225421460f6e Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208, 4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616, 78675968, 102400000, 214990848 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (262144 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: doneDer Plan
Ich mache aus der ersten Partition einen Datenspeicher für Backups. Darum habe ich auch in ext4 formatiert. In der Anleitung steht dann folgendes.
Backup files dump/Configuration Example (/etc/pve/storage.cfg)
dir: backup
path /mnt/backup
content backup
maxfiles 7Above configuration defines a storage pool called backup. That pool can be used to store up to 7 backups (maxfiles 7) per VM. The real path for the backup files is /mnt/backup/dump/....
Ok, das Probieren wir. Das Verzeichnis erstellt.
root@frank-mankel:~# mkdir /mnt/backup/ root@frank-mankel:~# mkdir /mnt/backup/dumpDann die Datei bearbeiten
nano /etc/pve/storage.cfgInhalt
dir: local path /var/lib/vz content iso,vztmpl,backup lvmthin: local-lvm thinpool data vgname pve content rootdir,images lvmthin: VM thinpool VM vgname VM content images,rootdir nodes frank-mankel dir: backup path /mnt/backup content backup maxfiles 7Das dir:backup habe ich hinzugefügt. Einmal F5 im Webinterface drücken.
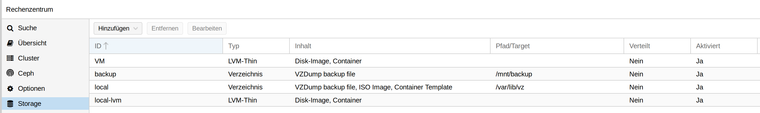
Schwupps, da ist das Backup-Verzeichnis.
Test, Backup von einem Container erstellt.
root@frank-mankel:~# ls -la /mnt/backup/dump total 381384 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 16:56 . drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jul 23 16:54 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 527 Jul 23 16:56 vzdump-lxc-102-2019_07_23-16_56_04.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 390521711 Jul 23 16:56 vzdump-lxc-102-2019_07_23-16_56_04.tar.lzoDie Struktur jetzt
root@frank-mankel:~# pvesm status Name Type Status Total Used Available % VM lvmthin active 488136704 23284120 464852583 4.77% backup dir active 57278576 3501916 50837372 6.11% local dir active 57278576 3501916 50837372 6.11% local-lvm lvmthin active 147275776 0 147275776 0.00%Das sieht so weit gut aus, hoffe ich

Wer aufgepasst hat, es ist noch eine Partition frei. Dafür gibt es auch schon einen Plan

-
Hoppla, da passt was nicht.
root@frank-mankel:~# pvesm status Name Type Status Total Used Available % VM lvmthin active 488136704 23284120 464852583 4.77% backup dir active 57278576 3501916 50837372 6.11% local dir active 57278576 3501916 50837372 6.11% local-lvm lvmthin active 147275776 0 147275776 0.00%Hier sieht man, das backup ca. 50GB groß ist. Da die Partition deutlich größer ist, fehlt da was!?? Kurz mal nachgedacht und gesucht.....

Der Eintrag in /etc/fstab muss natürlich auch vorhanden sein, so wie gewohnt. Danach
root@frank-mankel:~# pvesm status Name Type Status Total Used Available % VM lvmthin active 488136704 23284120 464852583 4.77% backup dir active 1921797220 77856 1824027568 0.00% local dir active 57278576 3502984 50836304 6.12% local-lvm lvmthin active 147275776 0 147275776 0.00%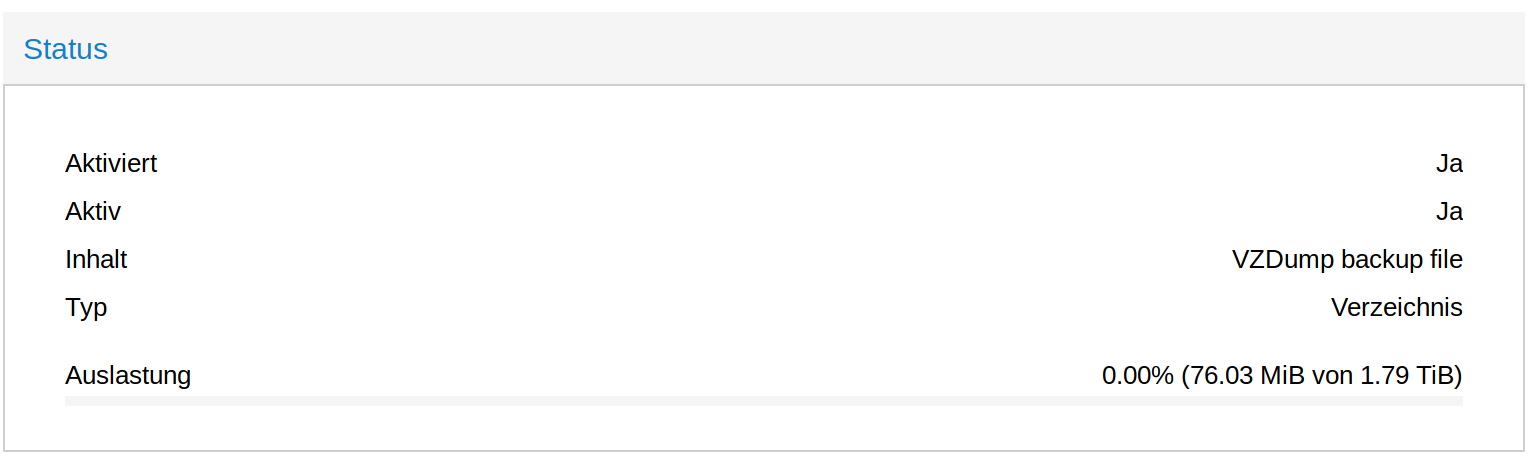
Mein vorhin erstelltes Backup war weg. Also aufpassen!!