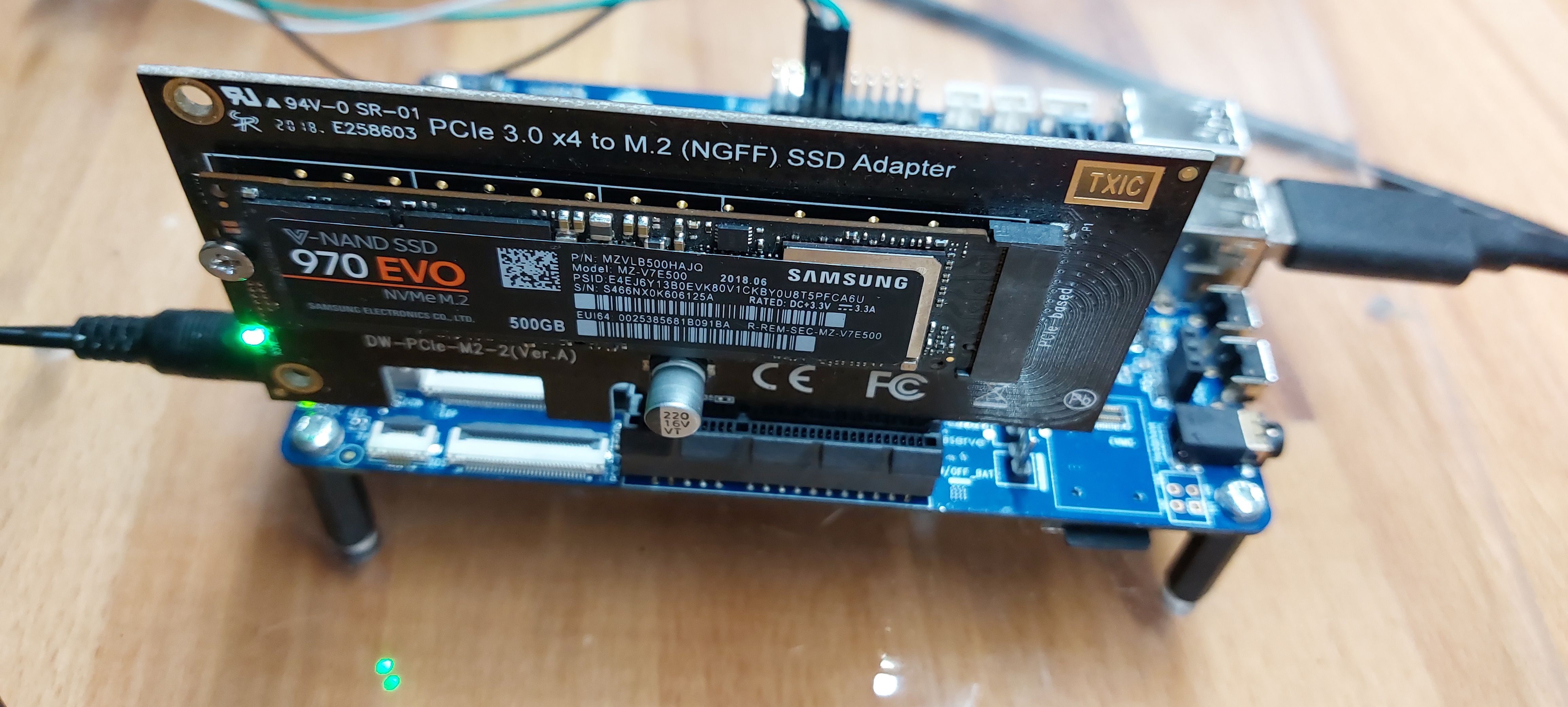
Quartz64 - Modell B - M.2 Anschluss
-
Ich habe mich auch gefragt, wie ich mir am Anfang die Fotos angeschaut habe, wie macht man die fest? Da waren keine Befestigungspunkte in der Platine.
Jo, wir brauchen auch keine

Nicht besonders elegant gelöst, oder? Von der Firma Radxa gibt es wohl für einen ähnlichen Fall einen Adapter. Ja, ich denke das ist notwendig.
Habe meine Platine jetzt aber incl. M.2 NVMe SSD auf mein Experimentierbrett befestigt. Das reicht für mich, sieht aber völlig hässlich aus.

-
Wer mich kennt weiß das es, wenn möglich, das erste ist was ausprobiert wird

Als Image habe ich das Build System vom Peter benutzt. Das installiert ein Debian auf der SD-Karte.
Hardware
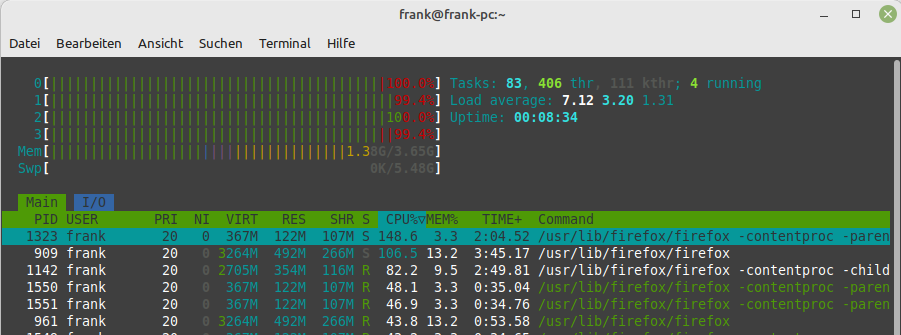
root@debian:/mnt/nvme# lspci 00:00.0 PCI bridge: Fuzhou Rockchip Electronics Co., Ltd Device 3566 (rev 01) 01:00.0 Non-Volatile memory controller: Samsung Electronics Co Ltd NVMe SSD Controller SM981/PM981 root@debian:/mnt/nvme# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/root 58G 4.7G 51G 9% / devtmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 2.0G 9.0M 1.9G 1% /run tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs 391M 0 391M 0% /run/user/1000 /dev/nvme0n1p1 458G 4.1G 431G 1% /mnt/nvmeSoftware
Kernel
root@debian:/mnt/nvme# uname -a Linux debian 5.17.0 #1 SMP PREEMPT Thu Apr 7 13:38:56 UTC 2022 aarch64 GNU/Linuxiozone
root@debian:/mnt/nvme# iozone -e -I -a -s 100M -r 4k -r 16k -r 512k -r 1024k -r 16384k -i 0 -i 1 -i 2 Iozone: Performance Test of File I/O Version $Revision: 3.429 $ Compiled for 64 bit mode. Build: linux Contributors:William Norcott, Don Capps, Isom Crawford, Kirby Collins Al Slater, Scott Rhine, Mike Wisner, Ken Goss Steve Landherr, Brad Smith, Mark Kelly, Dr. Alain CYR, Randy Dunlap, Mark Montague, Dan Million, Gavin Brebner, Jean-Marc Zucconi, Jeff Blomberg, Benny Halevy, Dave Boone, Erik Habbinga, Kris Strecker, Walter Wong, Joshua Root, Fabrice Bacchella, Zhenghua Xue, Qin Li, Darren Sawyer, Vangel Bojaxhi, Ben England, Vikentsi Lapa. Run began: Thu Jun 2 18:53:42 2022 Include fsync in write timing O_DIRECT feature enabled Auto Mode File size set to 102400 kB Record Size 4 kB Record Size 16 kB Record Size 512 kB Record Size 1024 kB Record Size 16384 kB Command line used: iozone -e -I -a -s 100M -r 4k -r 16k -r 512k -r 1024k -r 16384k -i 0 -i 1 -i 2 Output is in kBytes/sec Time Resolution = 0.000001 seconds. Processor cache size set to 1024 kBytes. Processor cache line size set to 32 bytes. File stride size set to 17 * record size. random random bkwd record stride kB reclen write rewrite read reread read write read rewrite read fwrite frewrite fread freread 102400 4 46839 71505 73664 72884 44939 69729 102400 16 119646 171084 172574 174223 126924 169845 102400 512 348734 358564 354061 357485 347061 358381 102400 1024 366048 368023 367023 374548 368630 370873 102400 16384 388125 387154 391752 397082 396637 378393dd
root@debian:/mnt/nvme# dd if=/dev/zero of=sd.img bs=1M count=4096 conv=fdatasync 4096+0 records in 4096+0 records out 4294967296 bytes (4.3 GB, 4.0 GiB) copied, 23.8028 s, 180 MB/s root@debian:/mnt/nvme# dd if=/dev/zero of=sd.img bs=4M count=4096 oflag=direct 4096+0 records in 4096+0 records out 17179869184 bytes (17 GB, 16 GiB) copied, 58.4993 s, 294 MB/s -
Ich hatte schon drauf getippt, das der Slot nur mit einer Lane angeschlossen ist.
<pgwipeout> It is a single lane pcie2 port.
Und damit ist das das erwartete Ergebnis
root@debian:/mnt/nvme# dd if=/dev/zero of=sd.img bs=4M count=4096 oflag=direct 4096+0 records in 4096+0 records out 17179869184 bytes (17 GB, 16 GiB) copied, 58.4993 s, 294 MB/sDas alles mit Debian 10, was man mit Peters Buildsystem installieren kann. Kann man aber auch bei Bedarf auf 11.3 hochziehen

root@debian:/etc# uname -a Linux debian 5.17.0 #1 SMP PREEMPT Thu Apr 7 13:38:56 UTC 2022 aarch64 GNU/Linux root@debian:/etc# cat debian_version 11.3 root@debian:/etc#