Quartz64 - Kühler
-
Im Moment aktuell noch überhaupt nicht nötig aber wollte es trotzdem hier mal vorstellen.
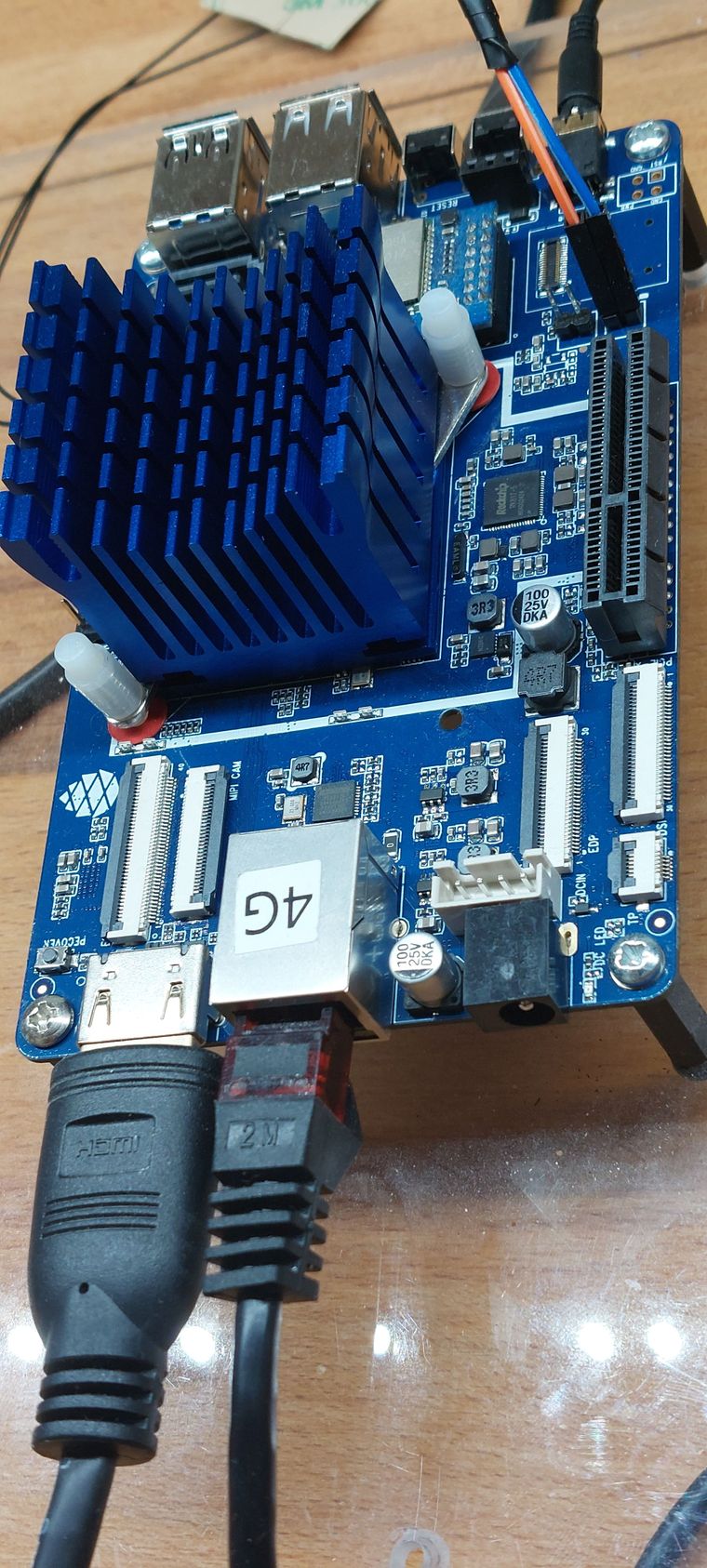
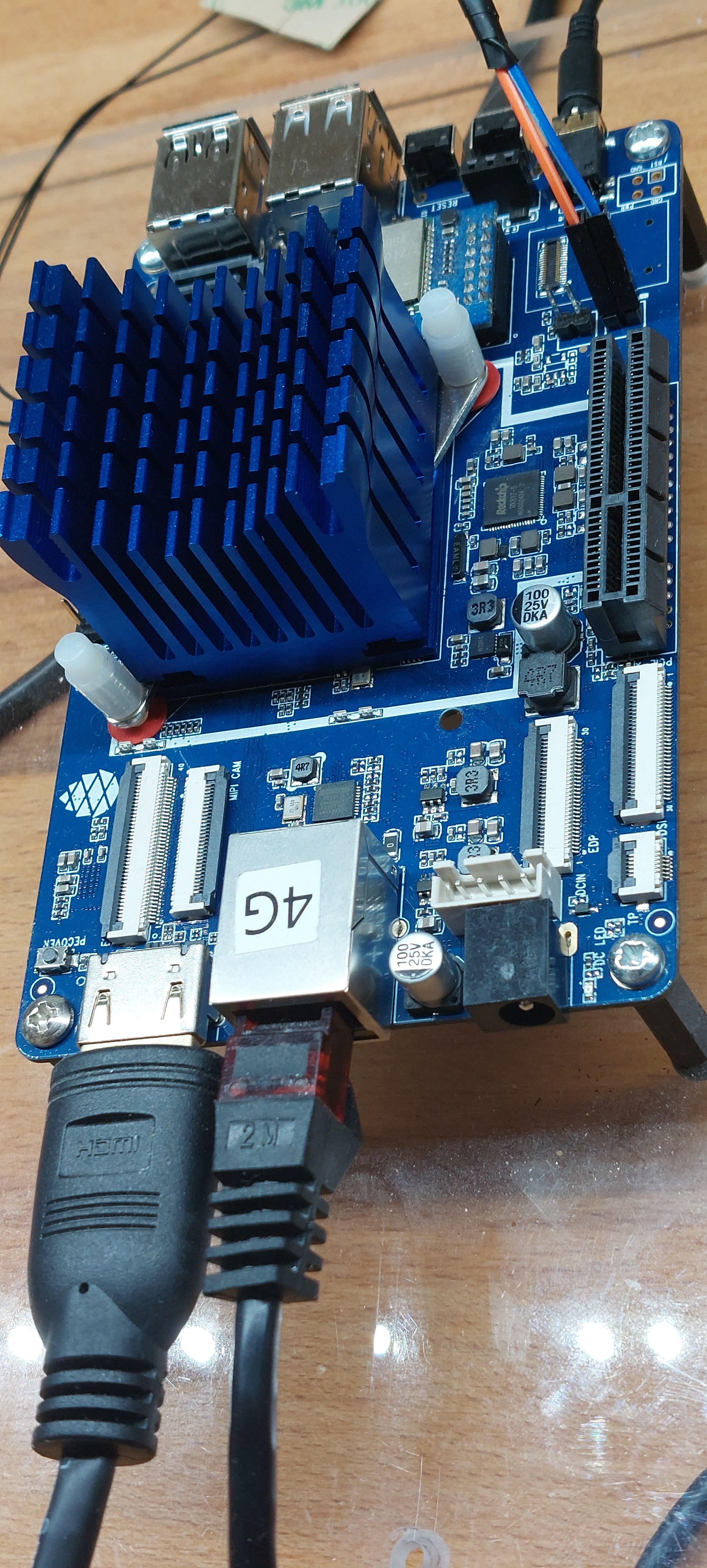
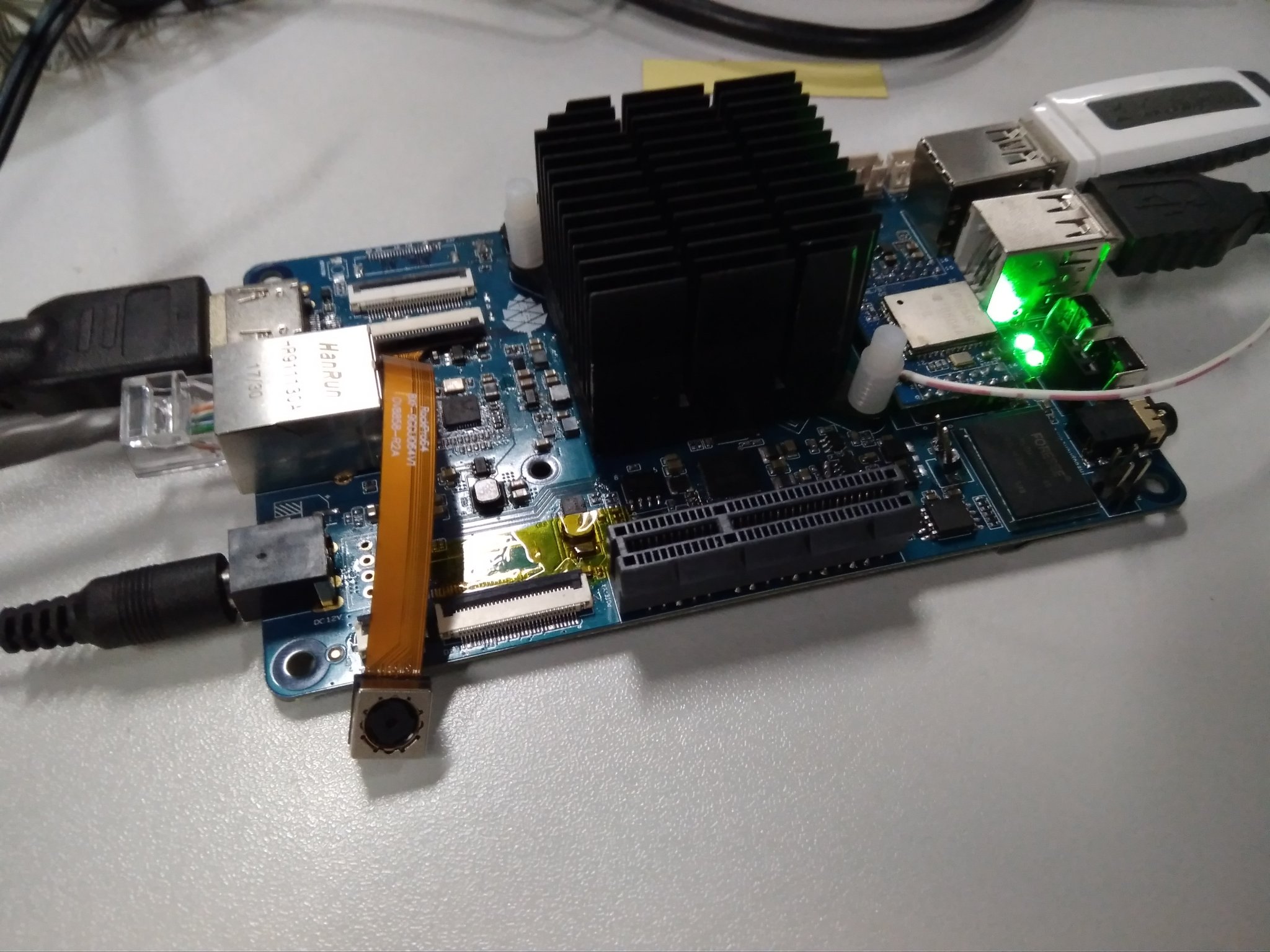
Auf dieses Board und auch genauso auf den ROCKPro64 passen ganz normale NorthBridge Kühler. Hier bei diesem Modell könnte man noch einen Lüfter drauf schrauben. Da ich keine Lüfter mag, mein NAS auf ROCKPro64 Basis hat auch nur einen Kühlkörper drauf, kommt da auch nie einer drauf.
-
Im Moment aktuell noch überhaupt nicht nötig aber wollte es trotzdem hier mal vorstellen.

Auf dieses Board und auch genauso auf den ROCKPro64 passen ganz normale NorthBridge Kühler. Hier bei diesem Modell könnte man noch einen Lüfter drauf schrauben. Da ich keine Lüfter mag, mein NAS auf ROCKPro64 Basis hat auch nur einen Kühlkörper drauf, kommt da auch nie einer drauf.
-
 F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Hardware am
F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Hardware am
-
 F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Quartz64 - A am
F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Quartz64 - A am
-
 F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Quartz64 am
F FrankM verschob dieses Thema von Quartz64 am
-
-
Quartz64 - Boot Order
Angeheftet Hardware -
-
Kernel 4.4.x
Angeheftet Images -
-
stretch-openmediavault-rockpro64
Verschoben Linux -
-