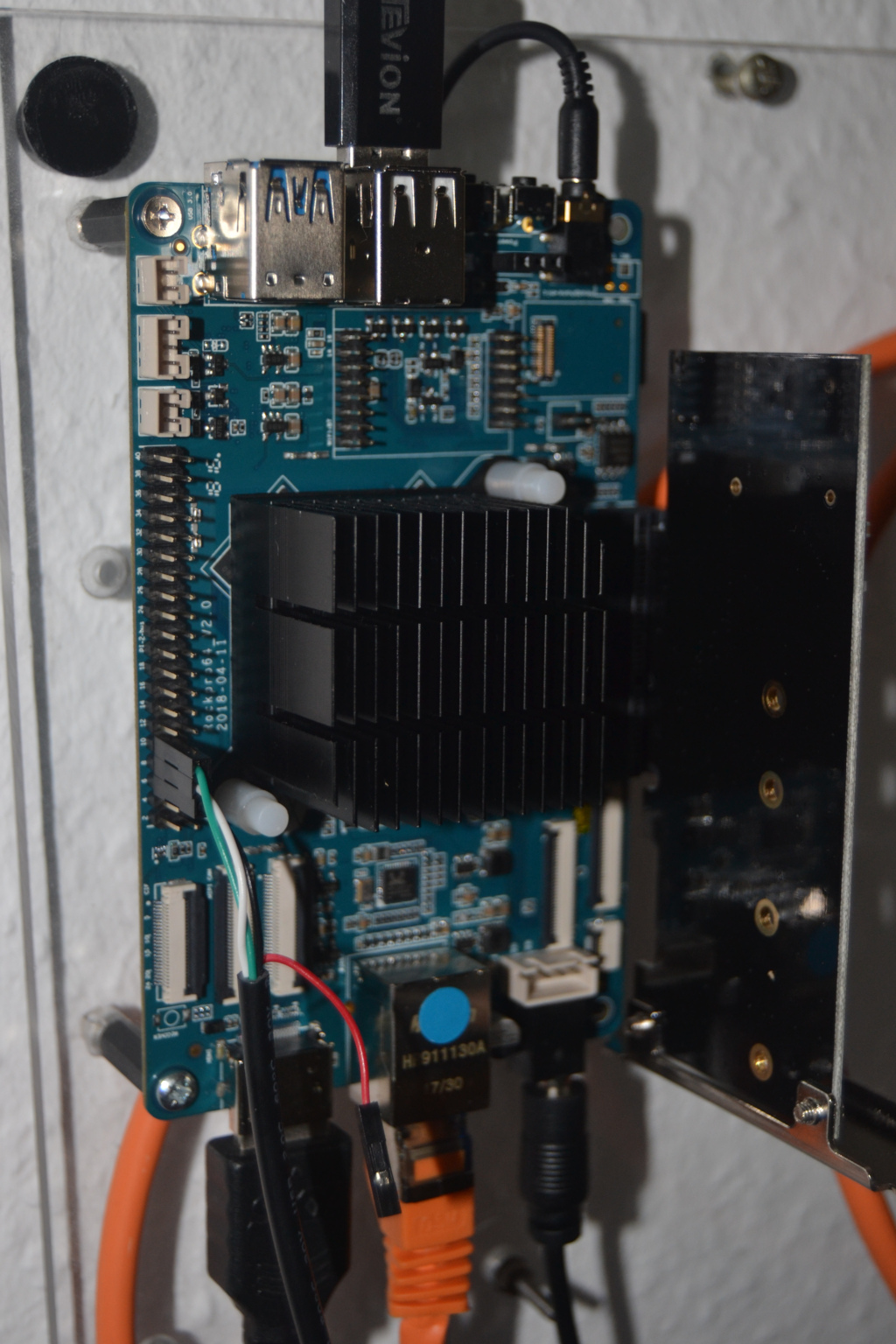
[HOWTO] ROCKPro64 - PCIe NVMe Karte mit Samsung 960 EVO m.2
-
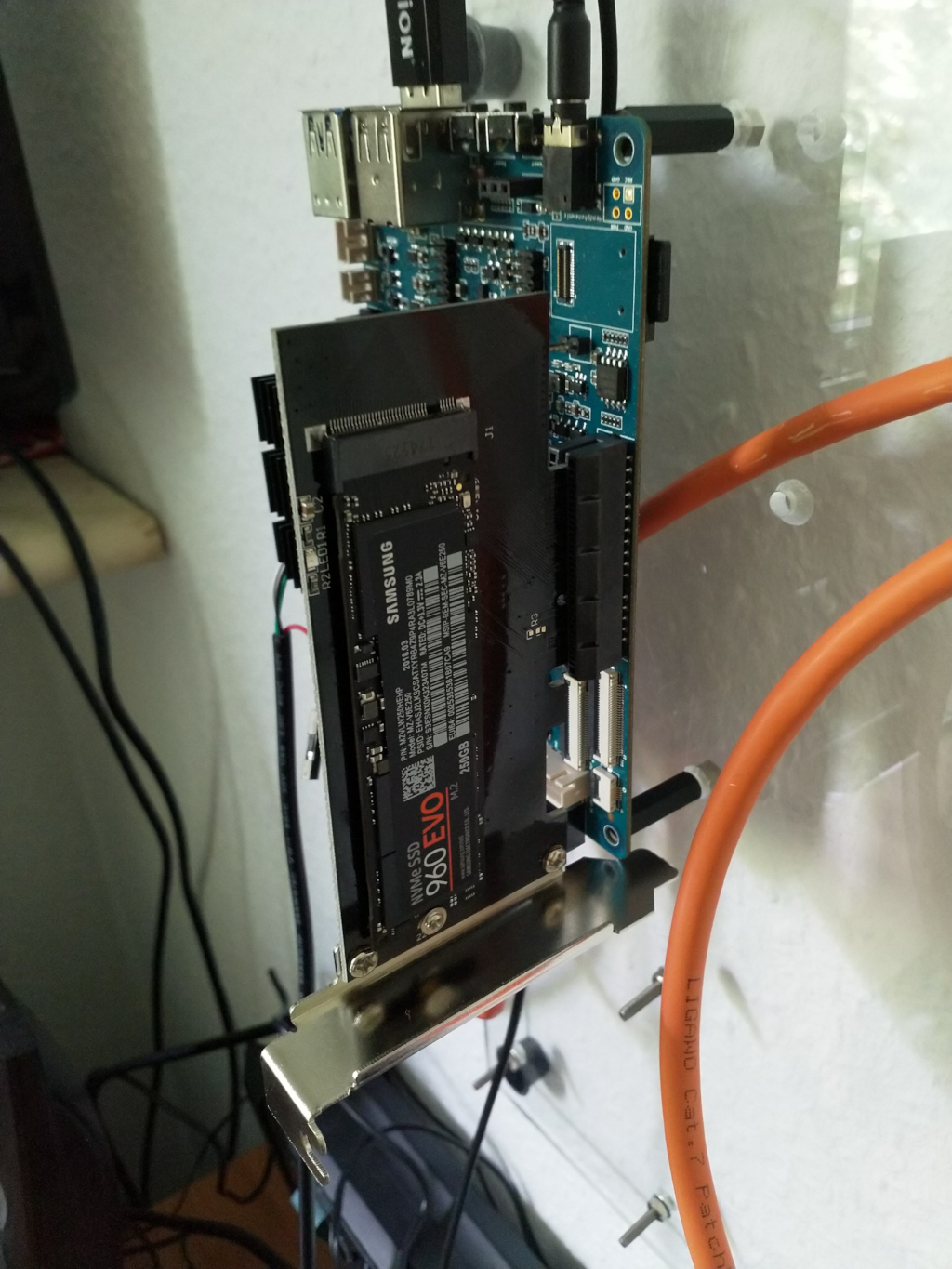
Das Bild sollte Euch ja mittlerweile bekannt vorkommen.
 Hier mal ein paar Dinge erklärt - Zielgruppe Einsteiger!
Hier mal ein paar Dinge erklärt - Zielgruppe Einsteiger!
Als erstes mal ein wichtiger Hinweis, von dieser Karte kann man aktuell nicht booten. Der U-Boot (Boatloader) unterstützt das zur Zeit nicht.
Ich nutze für die Versuche hier, die erste Version die den PCIe-Port zum Leben erweckt.
bionic-minimal-rockpro64-0.6.52-257-arm64.img.xzrock64@rockpro64:~$ uname -a Linux rockpro64 4.4.126-rockchip-ayufan-257 #1 SMP Sun Jun 10 18:30:43 UTC 2018 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/LinuxEin lspci zeigt uns ein paar Info's.
rock64@rockpro64:~$ lspci 00:00.0 PCI bridge: Rockchip Inc. RK3399 PCI Express Root Port Device 0100 01:00.0 Non-Volatile memory controller: Samsung Electronics Co Ltd NVMe SSD Controller SM961/PM961Hier sehen wir die Rockchip Bridge, das ist der PCIe-Slot und die Samsung SSD. Das gibt es auch in ausführlicher.
rock64@rockpro64:~$ sudo lspci -vvv [sudo] password for rock64: 00:00.0 PCI bridge: Rockchip Inc. RK3399 PCI Express Root Port Device 0100 (prog-if 00 [Normal decode]) Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx+ Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort+ <TAbort+ <MAbort+ >SERR+ <PERR+ INTx- Latency: 0 Interrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 238 Bus: primary=00, secondary=01, subordinate=01, sec-latency=0 I/O behind bridge: 00000000-00000fff Memory behind bridge: fa000000-fa0fffff Prefetchable memory behind bridge: 00000000-000fffff Secondary status: 66MHz- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- <SERR- <PERR- BridgeCtl: Parity- SERR- NoISA- VGA- MAbort- >Reset- FastB2B- PriDiscTmr- SecDiscTmr- DiscTmrStat- DiscTmrSERREn- Capabilities: [80] Power Management version 3 Flags: PMEClk- DSI- D1+ D2- AuxCurrent=0mA PME(D0+,D1+,D2-,D3hot+,D3cold-) Status: D0 NoSoftRst+ PME-Enable- DSel=0 DScale=0 PME+ Capabilities: [90] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable+ 64bit+ Address: 00000000fee30040 Data: 0000 Masking: 00000000 Pending: 00000000 Capabilities: [b0] MSI-X: Enable- Count=1 Masked- Vector table: BAR=0 offset=00000000 PBA: BAR=0 offset=00000008 Capabilities: [c0] Express (v2) Root Port (Slot+), MSI 00 DevCap: MaxPayload 256 bytes, PhantFunc 0 ExtTag- RBE+ DevCtl: Report errors: Correctable+ Non-Fatal+ Fatal+ Unsupported+ RlxdOrd+ ExtTag- PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop+ MaxPayload 128 bytes, MaxReadReq 512 bytes DevSta: CorrErr- UncorrErr- FatalErr- UnsuppReq- AuxPwr- TransPend- LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 5GT/s, Width x4, ASPM L1, Exit Latency L0s <256ns, L1 <8us ClockPM- Surprise- LLActRep- BwNot+ ASPMOptComp+ LnkCtl: ASPM L1 Enabled; RCB 64 bytes Disabled- CommClk- ExtSynch- ClockPM- AutWidDis- BWInt+ AutBWInt+ LnkSta: Speed 5GT/s, Width x2, TrErr- Train- SlotClk- DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt- SltCap: AttnBtn- PwrCtrl- MRL- AttnInd- PwrInd- HotPlug- Surprise- Slot #0, PowerLimit 0.000W; Interlock- NoCompl- SltCtl: Enable: AttnBtn- PwrFlt- MRL- PresDet- CmdCplt- HPIrq- LinkChg- Control: AttnInd Off, PwrInd Off, Power+ Interlock- SltSta: Status: AttnBtn- PowerFlt- MRL+ CmdCplt- PresDet- Interlock- Changed: MRL- PresDet- LinkState- RootCtl: ErrCorrectable- ErrNon-Fatal- ErrFatal- PMEIntEna+ CRSVisible- RootCap: CRSVisible- RootSta: PME ReqID 0000, PMEStatus- PMEPending- DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Range B, TimeoutDis+, LTR+, OBFF Via message ARIFwd+ DevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis-, LTR-, OBFF Disabled ARIFwd- LnkCtl2: Target Link Speed: 5GT/s, EnterCompliance- SpeedDis- Transmit Margin: Normal Operating Range, EnterModifiedCompliance- ComplianceSOS- Compliance De-emphasis: -6dB LnkSta2: Current De-emphasis Level: -6dB, EqualizationComplete-, EqualizationPhase1- EqualizationPhase2-, EqualizationPhase3-, LinkEqualizationRequest- Capabilities: [100 v2] Advanced Error Reporting UESta: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol- UEMsk: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol- UESvrt: DLP+ SDES+ TLP- FCP+ CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF+ MalfTLP+ ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol- CESta: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr- CEMsk: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr+ AERCap: First Error Pointer: 00, GenCap+ CGenEn- ChkCap+ ChkEn- Capabilities: [274 v1] Transaction Processing Hints Interrupt vector mode supported Device specific mode supported Steering table in TPH capability structure Kernel driver in use: pcieport 01:00.0 Non-Volatile memory controller: Samsung Electronics Co Ltd NVMe SSD Controller SM961/PM961 (prog-if 02 [NVM Express]) Subsystem: Samsung Electronics Co Ltd NVMe SSD Controller SM961/PM961 Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx+ Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx- Latency: 0 Interrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 237 Region 0: Memory at fa000000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16K] Capabilities: [40] Power Management version 3 Flags: PMEClk- DSI- D1- D2- AuxCurrent=0mA PME(D0-,D1-,D2-,D3hot-,D3cold-) Status: D0 NoSoftRst+ PME-Enable- DSel=0 DScale=0 PME- Capabilities: [50] MSI: Enable- Count=1/32 Maskable- 64bit+ Address: 0000000000000000 Data: 0000 Capabilities: [70] Express (v2) Endpoint, MSI 00 DevCap: MaxPayload 256 bytes, PhantFunc 0, Latency L0s unlimited, L1 unlimited ExtTag- AttnBtn- AttnInd- PwrInd- RBE+ FLReset+ SlotPowerLimit 0.000W DevCtl: Report errors: Correctable- Non-Fatal- Fatal- Unsupported- RlxdOrd+ ExtTag- PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop+ FLReset- MaxPayload 128 bytes, MaxReadReq 512 bytes DevSta: CorrErr- UncorrErr- FatalErr- UnsuppReq- AuxPwr+ TransPend- LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 8GT/s, Width x4, ASPM L1, Exit Latency L0s unlimited, L1 <64us ClockPM+ Surprise- LLActRep- BwNot- ASPMOptComp+ LnkCtl: ASPM L1 Enabled; RCB 64 bytes Disabled- CommClk- ExtSynch- ClockPM+ AutWidDis- BWInt- AutBWInt- LnkSta: Speed 5GT/s, Width x2, TrErr- Train- SlotClk+ DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt- DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Range ABCD, TimeoutDis+, LTR+, OBFF Not Supported DevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis-, LTR-, OBFF Disabled LnkCtl2: Target Link Speed: 8GT/s, EnterCompliance- SpeedDis- Transmit Margin: Normal Operating Range, EnterModifiedCompliance- ComplianceSOS- Compliance De-emphasis: -6dB LnkSta2: Current De-emphasis Level: -6dB, EqualizationComplete-, EqualizationPhase1- EqualizationPhase2-, EqualizationPhase3-, LinkEqualizationRequest- Capabilities: [b0] MSI-X: Enable+ Count=8 Masked- Vector table: BAR=0 offset=00003000 PBA: BAR=0 offset=00002000 Capabilities: [100 v2] Advanced Error Reporting UESta: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol- UEMsk: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol- UESvrt: DLP+ SDES+ TLP- FCP+ CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF+ MalfTLP+ ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol- CESta: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr- CEMsk: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr+ AERCap: First Error Pointer: 00, GenCap+ CGenEn- ChkCap+ ChkEn- Capabilities: [148 v1] Device Serial Number 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 Capabilities: [158 v1] Power Budgeting <?> Capabilities: [168 v1] #19 Capabilities: [188 v1] Latency Tolerance Reporting Max snoop latency: 0ns Max no snoop latency: 0ns Capabilities: [190 v1] L1 PM Substates L1SubCap: PCI-PM_L1.2+ PCI-PM_L1.1+ ASPM_L1.2+ ASPM_L1.1+ L1_PM_Substates+ PortCommonModeRestoreTime=10us PortTPowerOnTime=10us L1SubCtl1: PCI-PM_L1.2- PCI-PM_L1.1- ASPM_L1.2- ASPM_L1.1- T_CommonMode=0us LTR1.2_Threshold=0ns L1SubCtl2: T_PwrOn=10us Kernel driver in use: nvmeViele Dinge, wo man keine Ahnung von hat, auch ich nicht
 Aber, es gibt auch hier interessante Info's.
Aber, es gibt auch hier interessante Info's.LnkSta: Speed 5GT/s, Width x2, TrErr- Train- SlotClk+ DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt-Was sagt uns diese Zeile? Die SSD ist mit zwei Lanes (x2) an den Prozessor angebunden. Oder sollte? Der Adapter soll eigentlich x4 unterstützen.
Laut diesem Link hier, sollte sie maximal 800 MB/s schaufeln.
Etwas vom Thema abgekommen. Also zurück. Wir wissen jetzt das die SSD vorhanden ist. Ein sudo fdisk -l gibt folgendes aus.
rock64@rockpro64:~$ sudo fdisk -l Disk /dev/ram0: 4 MiB, 4194304 bytes, 8192 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/mmcblk0: 14.7 GiB, 15811477504 bytes, 30881792 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: gpt Disk identifier: 298096AF-4287-4988-B53A-24CDE27C1C8D Device Start End Sectors Size Type /dev/mmcblk0p1 64 8063 8000 3.9M Linux filesystem /dev/mmcblk0p2 8064 8191 128 64K Linux filesystem /dev/mmcblk0p3 8192 16383 8192 4M Linux filesystem /dev/mmcblk0p4 16384 24575 8192 4M Linux filesystem /dev/mmcblk0p5 24576 32767 8192 4M Linux filesystem /dev/mmcblk0p6 32768 262143 229376 112M Microsoft basic data /dev/mmcblk0p7 262144 30881758 30619615 14.6G Linux filesystem Disk /dev/nvme0n1: 232.9 GiB, 250059350016 bytes, 488397168 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/zram0: 323 MiB, 338722816 bytes, 82696 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/zram1: 323 MiB, 338722816 bytes, 82696 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/zram2: 323 MiB, 338722816 bytes, 82696 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/zram3: 323 MiB, 338722816 bytes, 82696 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/zram4: 323 MiB, 338722816 bytes, 82696 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/zram5: 323 MiB, 338722816 bytes, 82696 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytesDer interessante Teil.
Disk /dev/nvme0n1: 232.9 GiB, 250059350016 bytes, 488397168 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytesACHTUNG! Ab hier besteht die Gefahr von Datenverlust. Bitte vorher das Gehirn einschalten und denkt dran, ich übernehme kein Garantie für Eure Daten

Eine jungfräuliche Karte muss jetzt erst mal eingerichtet werden. Mit sudo fdisk /dev/nvme0n1
fdisk /dev/nvme0n1 Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.25.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Command (m for help): n Partition type p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) e extended (container for logical partitions) Select (default p): p Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 First sector (2048-488397168, default 2048): 2048 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-488397168, default 488397168): 488397168 Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 232,9 GiB. Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered. Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks.Danach noch formatieren.
mkfs.ext4 /dev/nvme0n1Mit
mount /dev/nvme0n1 /mnt/wird die SSD dann ins System eingehangen.
Speedtest
Schreibtest
rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=sd.img bs=1M count=4096 conv=fdatasync 4096+0 records in 4096+0 records out 4294967296 bytes (4.3 GB, 4.0 GiB) copied, 12.6595 s, 339 MB/s rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=sd.img bs=1M count=4096 conv=fdatasync 4096+0 records in 4096+0 records out 4294967296 bytes (4.3 GB, 4.0 GiB) copied, 12.6277 s, 340 MB/sLesetest
rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ sudo hdparm -tT /dev/nvme0n1 /dev/nvme0n1: Timing cached reads: 2562 MB in 2.00 seconds = 1280.89 MB/sec Timing buffered disk reads: 1734 MB in 3.00 seconds = 577.90 MB/secDas Ganze mal laut dieser Anleitung.
rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=tempfile bs=1M count=1024 conv=fdatasync,notrunc 1024+0 records in 1024+0 records out 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 3.41565 s, 314 MB/s rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches 3 rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ dd if=tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 1024+0 records in 1024+0 records out 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 1.62841 s, 659 MB/s rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ dd if=tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 1024+0 records in 1024+0 records out 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 0.701997 s, 1.5 GB/s rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ dd if=tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 1024+0 records in 1024+0 records out 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 0.664641 s, 1.6 GB/s rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ dd if=tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 1024+0 records in 1024+0 records out 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 0.681466 s, 1.6 GB/s rock64@rockpro64:/mnt$ dd if=tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 1024+0 records in 1024+0 records out 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 0.687785 s, 1.6 GB/sNun müsste man die Testergebnisse einschätzen können. Da das meine erste SSD in einem PCIe Steckplatz ist, kann ich das nicht so richtig. Fakt ist, eigentlich müsste da was mehr gehen. Ich überlasse mal die Einschätzung anderen. @tkaiser
Fazit:
Das könnte ein richtig interessantes SOC werden, ich träume jetzt mal was. Booten von der PCIe-SSD und an USB3 ein Datengrab. Könnte ein sehr vielversprechendes NAS werden oder was auch immer. Viel Spaß beim Testen!!
Und Danke an Kamil für seine Arbeit an diesem Linux-Image!
-
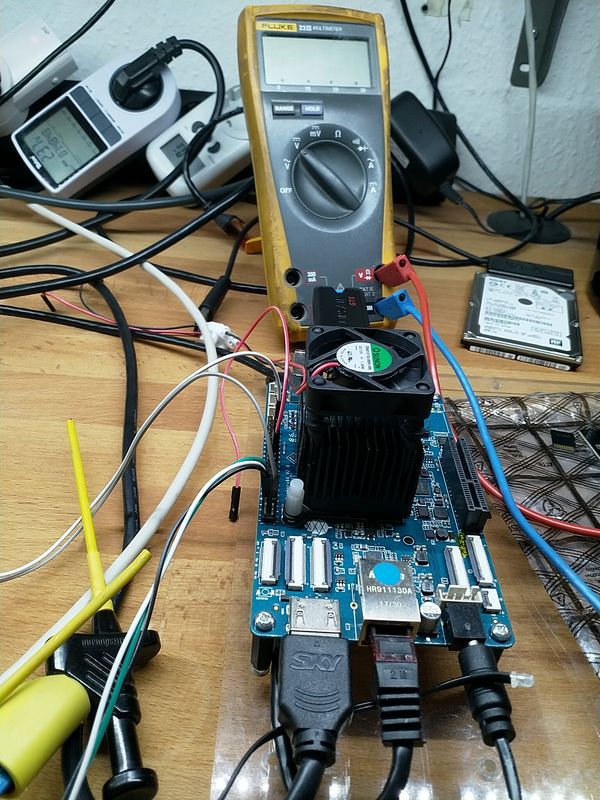
Ergänzung
Eine andere SATA-Karte und eine Riser-Karte mit angeschlossener GPU startet nicht.
rock64@rockpro64v2_1:~$ uname -a Linux rockpro64v2_1 4.4.132-1075-rockchip-ayufan-ga83beded8524 #1 SMP Thu Jul 26 08:22:22 UTC 2018 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/Linux