Python3 - Pipenv für die virtuelle Entwicklungsumgebung
Python3
2
Beiträge
1
Kommentatoren
471
Aufrufe
-
Python hat ein wirklich sehr groß entwickeltes Ökosystem, mit ganz vielen Tools, die man erst mal finden muss und dann im zweiten Step auch nutzen können muss.
Hier geht es heute um pipenv
Installation
sudo apt install pipenvVirtuelle Umgebung anlegen
Wir wechseln ins Projektverzeichnis
cd /home/$USER/projekt1Die Entwicklungsumgebung anlegen
pipenv --python 3.8Die Entwicklungsumgebung starten
frank@frank-MS-7C37:~/restic_ui$ pipenv shell Spawning environment shell (/bin/bash). Use 'exit' to leave. frank@frank-MS-7C37:~/restic_ui$ . /home/frank/.local/share/virtualenvs/restic_ui-RwXjz-0W/bin/activate (restic_ui-RwXjz-0W) frank@frank-MS-7C37:~/restic_ui$ pipenv Usage: pipenv [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]... Options: --where Output project home information. --venv Output virtualenv information. --py Output Python interpreter information. --envs Output Environment Variable options. --rm Remove the virtualenv. --bare Minimal output. --completion Output completion (to be eval'd). --man Display manpage. --three / --two Use Python 3/2 when creating virtualenv. --python TEXT Specify which version of Python virtualenv should use. --site-packages Enable site-packages for the virtualenv. --version Show the version and exit. -h, --help Show this message and exit. Usage Examples: Create a new project using Python 3.6, specifically: $ pipenv --python 3.6 Install all dependencies for a project (including dev): $ pipenv install --dev Create a lockfile containing pre-releases: $ pipenv lock --pre Show a graph of your installed dependencies: $ pipenv graph Check your installed dependencies for security vulnerabilities: $ pipenv check Install a local setup.py into your virtual environment/Pipfile: $ pipenv install -e . Use a lower-level pip command: $ pipenv run pip freeze Commands: check Checks for security vulnerabilities and against PEP 508 markers provided in Pipfile. clean Uninstalls all packages not specified in Pipfile.lock. graph Displays currently–installed dependency graph information. install Installs provided packages and adds them to Pipfile, or (if none is given), installs all packages. lock Generates Pipfile.lock. open View a given module in your editor. run Spawns a command installed into the virtualenv. shell Spawns a shell within the virtualenv. sync Installs all packages specified in Pipfile.lock. uninstall Un-installs a provided package and removes it from Pipfile. update Runs lock, then sync. -
Ich ko... immer, wenn ich mein VSCodium neu installieren muss. Das größte Problem dabei ist immer, das ich fast immer vergesse den Python Interpreter zu setzen.
"CTRL+SHIFT+P" and choose the correct python interpreter.
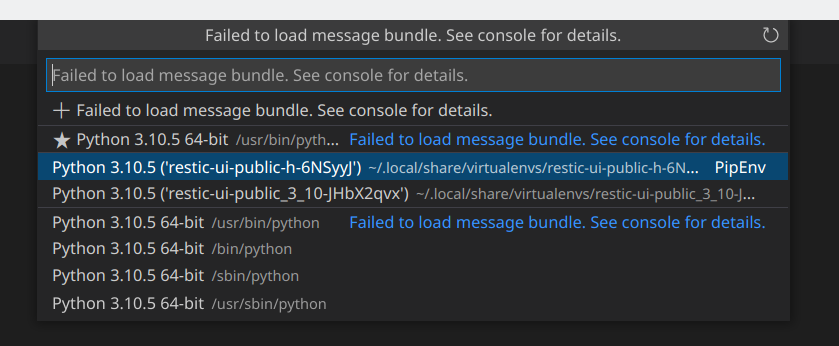
Danach startet das Python Programm auch wieder aus der richtigen Entwicklungsumgebung

-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Wichtige Links
Angeheftet Python3 -