Ayufan Release 0.7.12
-
Kamil arbeitet gerade am nächsten Release 0.7.12, der letzte Versuch ist noch gescheitert aber wir hoffen mal das wir bald neues Futter zum Testen bekommen. Ein paar Info's kann man schon bekommen.
Das wird drin sein
LATEST_UBOOT_VERSION=2017.09-rockchip-ayufan-1035-gd646df03ac
LATEST_KERNEL_VERSION=4.4.154-1132-rockchip-ayufan-g8260cd865508
LATEST_PACKAGE_VERSION=0.7-44Also, eine neue u-boot Version und ein aktualisierter Kernel.
- 0.7.12: Rebased mainline kernel,
- 0.7.12: Rockchip kernel has patches for enabling sdio0 and pcie concurrently,
- 0.7.12: A bunch of dependencies updates,
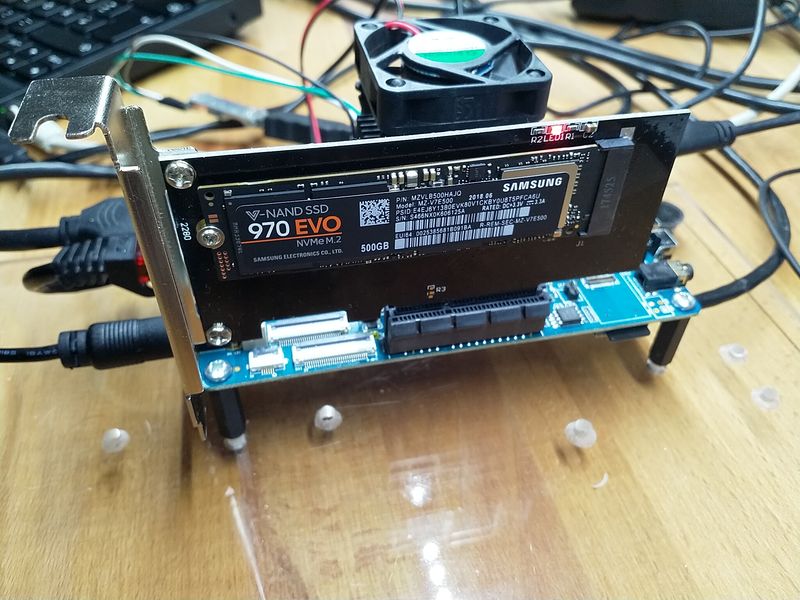
Da bin ich ja mal extrem gespannt ob das sdio0 und das pcie zusammen funktioniert!
Quelle: https://github.com/ayufan-rock64/linux-build/commit/5542a8a0e6f2ee8a27f3b4ad4dc60e0adf0f3bbb
-
Dafür andere Probleme


0.7.12_with_pcie_nvme_ssd - Pastebin.com
Pastebin.com is the number one paste tool since 2002. Pastebin is a website where you can store text online for a set period of time.
Pastebin (pastebin.com)
Aktuell nicht zu empfehlen!
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Images 0.6.x
Verschoben Images