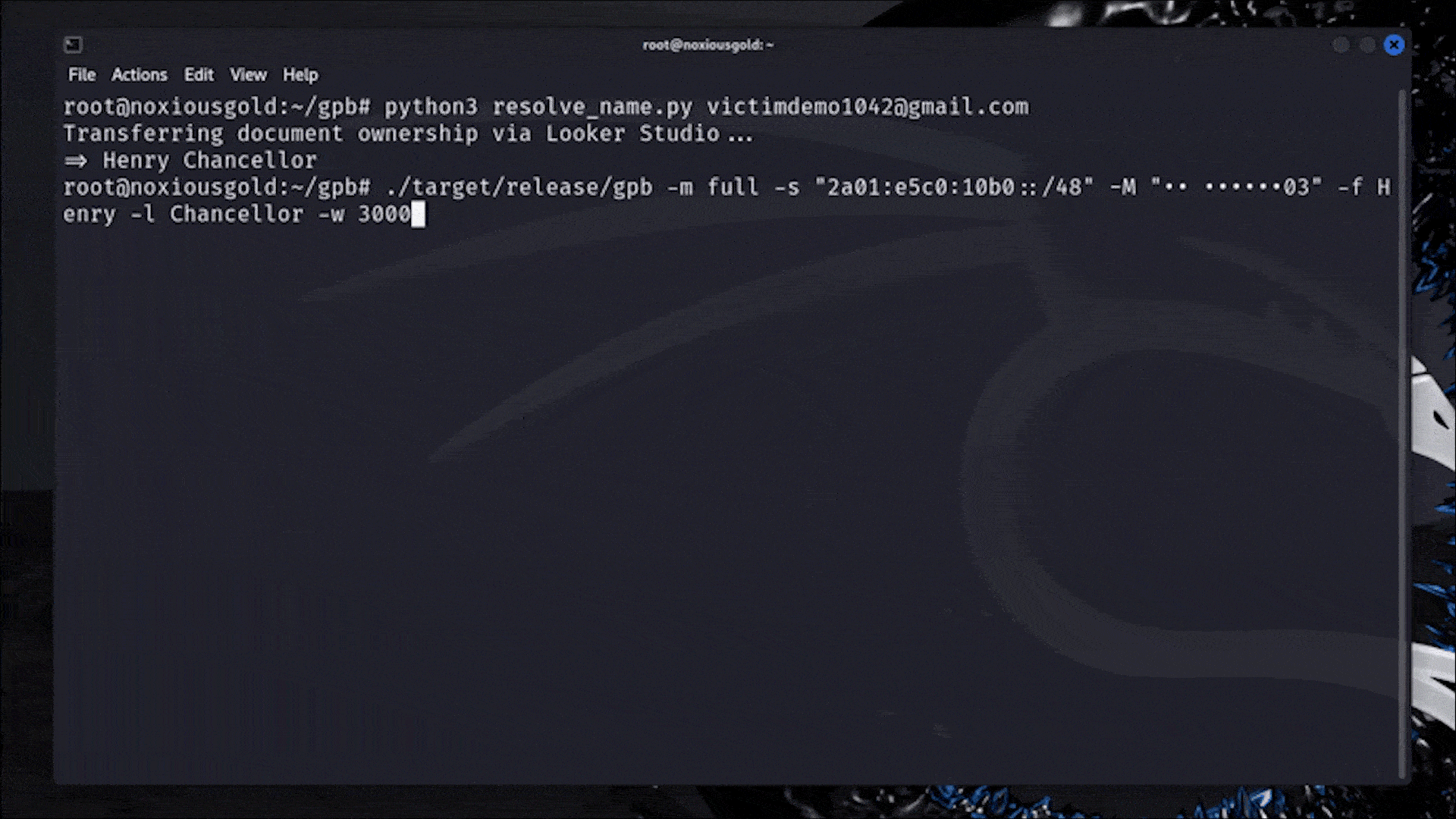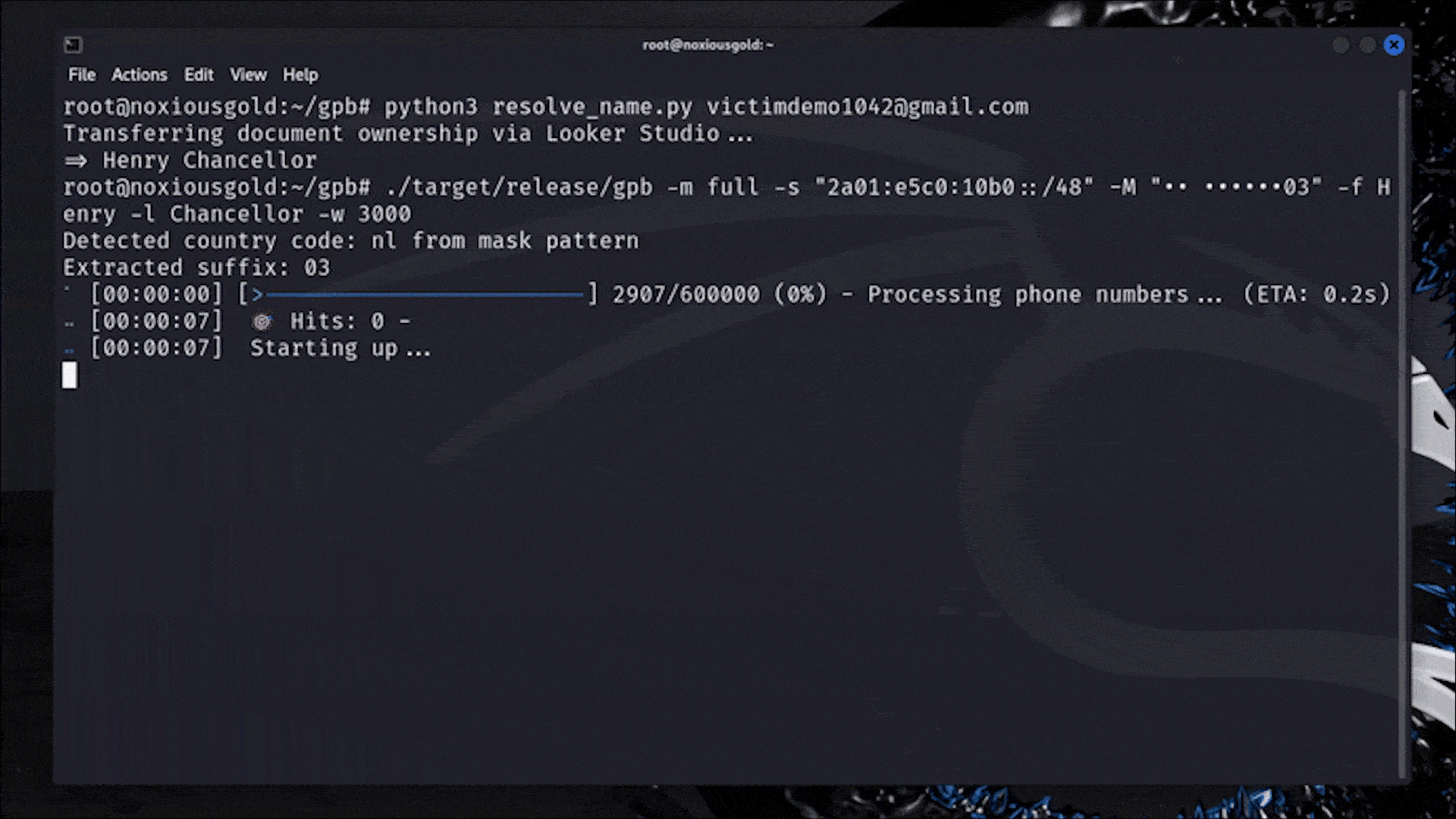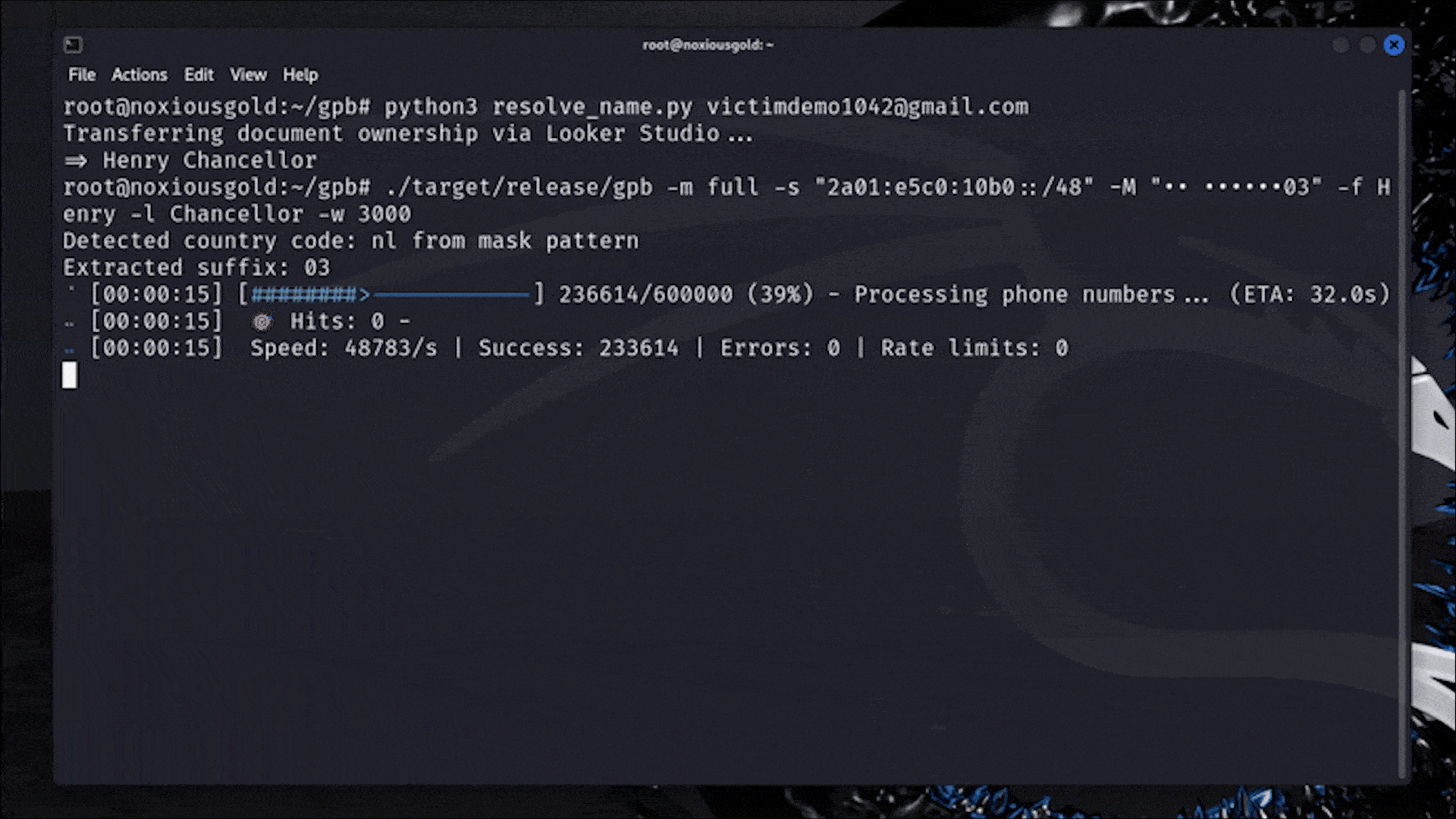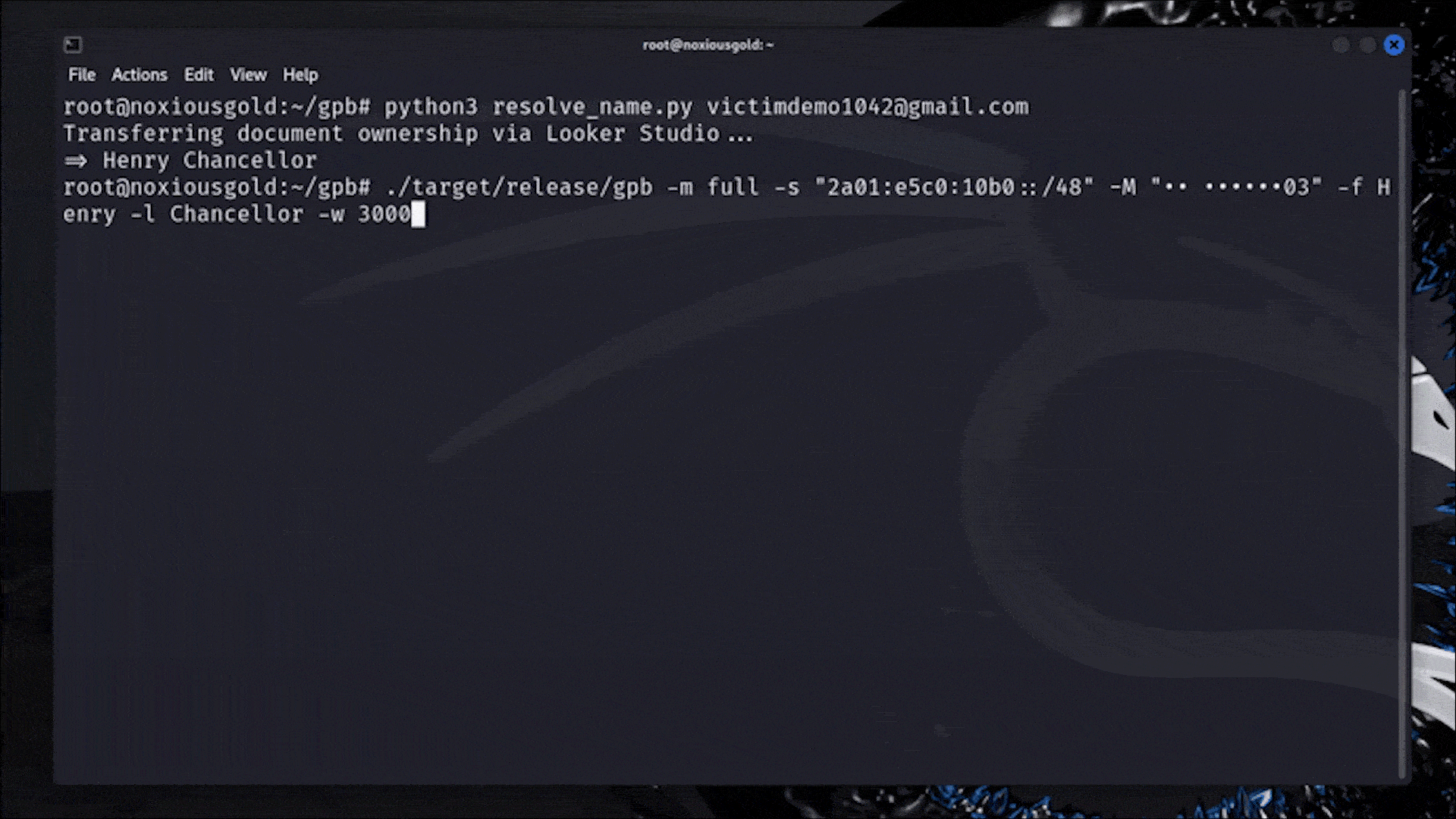
A Researcher Figured Out How to Reveal Any Phone Number Linked to a Google Account
-
Still are. I got a phone book delivered a week ago, I shit thee not. Granted I'm on a small island and the book is small too. But like, you can pay to have your number removed from the book. Can you have it removed from this? Not to mention all the 2FA stuff that can be connected to the phone number. Someone clones your number or takes it and suddenly they've got access to a whole lot of your login stuff.
Pay to have it removed! That sounds like blackmail doxing.
-
It would be even cooler if we had a right to privacy
No doubt, lucky us, we get neither...
-
Right, but when everyone got phone books, those were only shared locally in the town. It would be pretty hard to figure out someones phone number from across the state/country without the internet unless you knew someone in the town.
You could also pay to be unlisted, which is a luxury long since gone. How cool would it be to make your data 'unlisted' by paying a small monthly fee.
Phone books from outside my region were available at the library; that place where they store a consolidated collection of books for just anyone to sign out and use.
-
God, I hate security "researchers". If I posted an article about how to poison everyone in my neighborhood, I'd be getting a knock on the door. This kind of shit doesn't help anyone. "Oh but the state-funded attackers, remember stuxnet". Fuck off.
This disclosure was from last year and the exploit was patched before the researcher published the findings to the public.
-
Casually rotating 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 IP addresses to bypass rate limits.
I am not in IT security, but find it fascinating what clever tricks people use to break (into) stuff.
In a better world, we might use this energy for advancing humanity instead of looking how we can hurt each other. (Not saying the author is doing that, just lamenting that ITS is necessary due to hostile actors in this world. )
If you know how to hurt others, you can learn how to prevent that way of hurting others.
-
F. This will be moved to an OSINT tool within a week, and scraped into a darkweb database by next Friday.
-
I set up my GranCentral, now Google Voice, account using a VoIP number from a company that went defunct many years ago. My Google accounts use said Google Voice phone number to validate because GrandCentral wasn't owned by Google back then. I assume this use case is so small, there is no point fixing it. So essentially, my accounts fall into a loop where google leads to google, etc.
heh
I did something of the opposite. I had a Verizon number. I moved it to Google voice. I had a second Google voice number that then became a google fi number. So now I have a Verizon coded google voice number (that my bank accepts etc), and a google fi number that was originally a google voice number. I'm curious how this honestly effects me. My work numbers have never been associated with my personal accounts so there's that.
-
Casually rotating 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 IP addresses to bypass rate limits.
I am not in IT security, but find it fascinating what clever tricks people use to break (into) stuff.
In a better world, we might use this energy for advancing humanity instead of looking how we can hurt each other. (Not saying the author is doing that, just lamenting that ITS is necessary due to hostile actors in this world. )
Those are IPv6 addresses that work a bit differently than IPv4. Most customers only get assigned a single IPv4 address, and even a lot of big data centers only have one or two blocks of 256 addresses. The smallest allocation of IPv6 for a single residential customer is typically a contiguous block of the 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 addresses mentioned.
If Google's security team is even marginally competent, they will recognize those contiguous blocks and treat them as they would a single IPv4 address. Every address in that block has the same prefix, and it's actually easier to track on those prefixes than on the entire address.
-
Casually rotating 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 IP addresses to bypass rate limits.
I am not in IT security, but find it fascinating what clever tricks people use to break (into) stuff.
In a better world, we might use this energy for advancing humanity instead of looking how we can hurt each other. (Not saying the author is doing that, just lamenting that ITS is necessary due to hostile actors in this world. )
This doesn't really work in real life since IPv6 rate limiting is done per /64 block, not per individual IP address. This is because /64 is the smallest subnet allowed by the IPv6 spec, especially if you want to use features like SLAAC and privacy extensions (which most home users would be using)
SLAAC means that devices on the network can assign their own IPv6. It's like DHCP but is stateless and doesn't need a server.
Privacy extensions means that the IPv6 address is periodically changed to avoid any individual device from being tracked. All devices on an IPv6 network usually have their own public IP, which fixes some things (NAT and port forwarding aren't needed any more) but has potential privacy issues if one device has the same IP for a long time.
-
Ipv6 catching strays
Usually is. Still common among network admins to hear dumb shit like IPv6 being less secure because no NAT.

 ️
️ -
Phone books from outside my region were available at the library; that place where they store a consolidated collection of books for just anyone to sign out and use.
I don't remember that, however it doesn't surprise me at least for a radius around your area. I'd be surprised if they had all of them from all the states
-
F. This will be moved to an OSINT tool within a week, and scraped into a darkweb database by next Friday.
I think you missed the part at the very end of the page that showed the timeline of them reporting the vulnerability back in April, being rewarded for finding the vulnerability, the vulnerability being patched in May, and being allowed to publicize the vulnerability as of today.
-
F. This will be moved to an OSINT tool within a week, and scraped into a darkweb database by next Friday.
Well at the bottom of the article he shows the bug report timeline has been complete, so it's likely already fixed.
-
Usually is. Still common among network admins to hear dumb shit like IPv6 being less secure because no NAT.

 ️
️If NAT is your “firewall”, you have bigger problems!
-
$5,000
This is like 1/10th of what a good blackhat hacker would have gotten out of it.
-
I keep telling people, it's a matter of when, not if.
Do not trust corporations.
-
Google, Apple, and rest of big tech are pregnable despite their access to vast amounts of capital, and labor resources.
I used to be a big supporter of using their "social sign on" (or more generally speaking, single sign on) as a federated authentication mechanism. They have access to brilliant engineers thus naively thought - "well these companies are well funded, and security focused. What could go wrong having them handle a critical entry point for services?”
Well as this position continues to age poorly, many fucking aspects can go wrong!
- These authentication services owned by big tech are much more attractive to attack. Finding that one vulnerability in their massive attack vector is difficult but not impossible.
- If you use big tech to authenticate to services, you are now subject to the vague terms of service of big tech. Oh you forgot to pay Google store bill because card on file expired? Now your Google account is locked out and now lose access to hundreds of services that have no direct relation to Google/Apple
- Using third party auth mechanisms like Google often complicate the relationship between service provider and consumer. Support costs increase because when a 80 yr old forgot password or 2FA method to Google account. They will go to the service provider instead of Google to fix it. Then you spend inordinate amounts of time/resources trying to fix issue. These costs eventually passed on to customer in some form or another
Which is why my new position is for federated authentication protocols. Similar to how Lemmy and the fediverse work but for authentication and authorization.
Having your own IdP won’t fix the 3rd issue, but at least it will alleviate 1st and 2nd concerns
They have access to brilliant engineers
Not really.
-
Damn that's interesting. I like how they walked through step by step how they got the exploit to work. This is what actual real hacking is like, but much less glamorous than what you see in the movies.
-
I don't remember that, however it doesn't surprise me at least for a radius around your area. I'd be surprised if they had all of them from all the states
You could just have them borrow one from whatever other library had it. Hell, you could just call the phone company and order the one you want yourself. Fuck, you could just call 411 and have them look it up for you right then.
-
Phone books from outside my region were available at the library; that place where they store a consolidated collection of books for just anyone to sign out and use.
I once used one to look up my friend from summer camp. He lived in New York City and I didn't live anywhere close
Library had a bunch of NYC phonebooks