60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
-
This post did not contain any content.
Survey: 60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
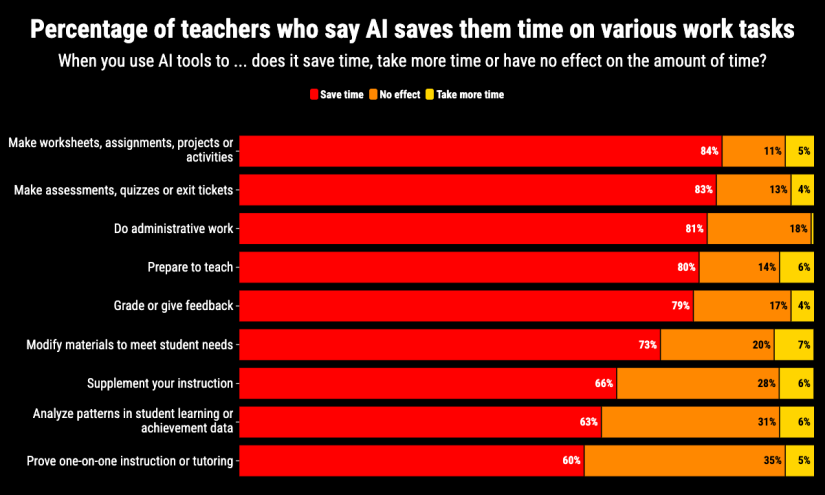
New study of 2,232 U.S. public school teachers found they use artificial intelligence tools to create worksheets, modify student materials, make tests

(www.the74million.org)
-
This post did not contain any content.

Survey: 60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
New study of 2,232 U.S. public school teachers found they use artificial intelligence tools to create worksheets, modify student materials, make tests

(www.the74million.org)
Lmao we're boned
-
This post did not contain any content.

Survey: 60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
New study of 2,232 U.S. public school teachers found they use artificial intelligence tools to create worksheets, modify student materials, make tests

(www.the74million.org)
Using AI to quickly generate quizzes is cool, it saves time having to copy/paste basic questions from elsewhere
On the other hand, screw teachers using LLMs for grading. It's unreliable and makes mistakes. Do your job.
-
Using AI to quickly generate quizzes is cool, it saves time having to copy/paste basic questions from elsewhere
On the other hand, screw teachers using LLMs for grading. It's unreliable and makes mistakes. Do your job.
Teachers use AI to generate assignments, kids use AI to generate answers, teachers use AI to grade answers.
Yeah, we're cooked.
-
Teachers use AI to generate assignments, kids use AI to generate answers, teachers use AI to grade answers.
Yeah, we're cooked.
Thank you for submitting your final exam for AP American History. ChatGPT 5-TeacherEdition graded your Llama 6.3o answers to be 25% incorrect. This determination is only appealable by confirming an error in grading with a Gemini X-5-level grading-appeal service, with a Standard Reliability rating of 7.5 or higher. Our system notes from your records that this service is not available to your income tier.
Your future profession is selected as: Meat packer.
Have a nice day.
-
Lmao we're boned
Yes, we are. I have a maths teacher friend, who complains endlessly about the shit that Sam Altman lies about, and yet they pay for ChatGPT and refuse to simply not use it. I swear it's worse than meth in terms of how it grabs some people.
-
Yes, we are. I have a maths teacher friend, who complains endlessly about the shit that Sam Altman lies about, and yet they pay for ChatGPT and refuse to simply not use it. I swear it's worse than meth in terms of how it grabs some people.
I literally only ever use it to rewrite things I’ve already written or to get my thoughts started when I’m having writer’s block (professional writing - not a creative writer). I really don’t understand why people use it beyond that. I don’t like having to check its homework all the damn time
Basically it’s just a tool for getting me to phrase or look at something differently. I can get tunnel vision when I’m writing or trying to come up with ideas.
-
This post did not contain any content.

Survey: 60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
New study of 2,232 U.S. public school teachers found they use artificial intelligence tools to create worksheets, modify student materials, make tests

(www.the74million.org)
How much of it did they fact check?
-
This post did not contain any content.

Survey: 60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
New study of 2,232 U.S. public school teachers found they use artificial intelligence tools to create worksheets, modify student materials, make tests

(www.the74million.org)
There is value in AI, blindly rejecting all use is just as stupid as blindly embracing all uses. Teacher are especially important in shaping how the next generation will be using it. They are at the front, discovering how students uses it what is good and what is bad. Finding way to improve their teaching is a good use. Saving time grading is a bad use.
Which ai service to use or not and why is another important facet. A trustworthy service can enshitify real fast, teaching what to look for is also something necessary. Nobody is fully competent in that matter, it still need to be discovered.
-
Using AI to quickly generate quizzes is cool, it saves time having to copy/paste basic questions from elsewhere
On the other hand, screw teachers using LLMs for grading. It's unreliable and makes mistakes. Do your job.
LLM's use a lot of energy and software that keeps a bank of questions and can generate a list is common. Really though your lesson planning should start with the assessment.
-
There is value in AI, blindly rejecting all use is just as stupid as blindly embracing all uses. Teacher are especially important in shaping how the next generation will be using it. They are at the front, discovering how students uses it what is good and what is bad. Finding way to improve their teaching is a good use. Saving time grading is a bad use.
Which ai service to use or not and why is another important facet. A trustworthy service can enshitify real fast, teaching what to look for is also something necessary. Nobody is fully competent in that matter, it still need to be discovered.
Is there enough value in AI to justify burning down the planet for it?
-
This post did not contain any content.

Survey: 60% of Teachers Used AI This Year and Saved up to 6 Hours of Work a Week
New study of 2,232 U.S. public school teachers found they use artificial intelligence tools to create worksheets, modify student materials, make tests

(www.the74million.org)
i'm reporting the post because it is from a blatant disinfo house that spreads rhetoric about "critical race theory" and other obvious dogwhistles
it is not a coincidence that AI is being pushed so hard by conservative racists
-
Is there enough value in AI to justify burning down the planet for it?
Telling people to stop doing something because it burns the planet doesn't really changes their mind in general unfortunately. Best you can do is put the numbers in their face so that they can't avoid the truth. But that only works on people who care.
-
Is there enough value in AI to justify burning down the planet for it?
I actually don't know that much about LLM's. I do know they require a ton of energy to train the models. But once those are trained, the smaller models especially, don't require that much to run, right? I once tried to run a local one to see how much it took, and my gpu maxed out for a few seconds and the LLM spit out text and it was done. While when playing games, the gpu maxes out for hours.
Again, i don't know super much about them as i have only used it a few times over the years to break down big tasks into smaller tasks for my AuDHD when i am very overwhelmed, and it was kinda nice for that.
The image generation stuff is pretty bad though from what i have read. Plus it steals peoples art. Fuck that shit.
Please do tell me if i understand wrong. Because i don't want to contribute to a bunch of bad shit ruining the climate.
-
LLM's use a lot of energy and software that keeps a bank of questions and can generate a list is common. Really though your lesson planning should start with the assessment.
LLMs don't use that much energy once trained. We run some models on a Mac Mini at work, and that thing sips power. Since education materials don't change much, there's no reason to need an up-to-date model for most subjects.
-
Telling people to stop doing something because it burns the planet doesn't really changes their mind in general unfortunately. Best you can do is put the numbers in their face so that they can't avoid the truth. But that only works on people who care.
That is sadly the truth with many things. People just don't care unless it personally affects them. And even then it depends if it hits hard enough
 .
. -
There is value in AI, blindly rejecting all use is just as stupid as blindly embracing all uses. Teacher are especially important in shaping how the next generation will be using it. They are at the front, discovering how students uses it what is good and what is bad. Finding way to improve their teaching is a good use. Saving time grading is a bad use.
Which ai service to use or not and why is another important facet. A trustworthy service can enshitify real fast, teaching what to look for is also something necessary. Nobody is fully competent in that matter, it still need to be discovered.
Exactly. If anyone is going to be using AI at the forefront, it should be teachers, for two reasons:
- so they can teach students its proper use because it will come up
- education is closely tracked, so we can see the impact of teachers relying on AI in student outcomes
I think this is fantastic!
-
i'm reporting the post because it is from a blatant disinfo house that spreads rhetoric about "critical race theory" and other obvious dogwhistles
it is not a coincidence that AI is being pushed so hard by conservative racists
? Media bias fact check says it's left-center w/ high factual accuracy. The poll itself is from Gallup, which is quite reputable, and The Walton Family Foundation, which is also reputable.
Are you thinking of something else?
-
I actually don't know that much about LLM's. I do know they require a ton of energy to train the models. But once those are trained, the smaller models especially, don't require that much to run, right? I once tried to run a local one to see how much it took, and my gpu maxed out for a few seconds and the LLM spit out text and it was done. While when playing games, the gpu maxes out for hours.
Again, i don't know super much about them as i have only used it a few times over the years to break down big tasks into smaller tasks for my AuDHD when i am very overwhelmed, and it was kinda nice for that.
The image generation stuff is pretty bad though from what i have read. Plus it steals peoples art. Fuck that shit.
Please do tell me if i understand wrong. Because i don't want to contribute to a bunch of bad shit ruining the climate.
- It's not like the companies train one model and they use it for months until they need new version. They train new models all the time to update them and test new ideas.
- They don't use small models. Typical LLMs offered by ChatGPT or Claude are the big ones
- They process thousands of queries per second so their GPUs are maxed out all the time, not just for few seconds.
-
? Media bias fact check says it's left-center w/ high factual accuracy. The poll itself is from Gallup, which is quite reputable, and The Walton Family Foundation, which is also reputable.
Are you thinking of something else?
There is no room here for your credulity. No, polls are not accurate. No, the Walmart tax dodge charity foundation is not "reputable."








