Scientists make game-changing breakthrough that could slash costs of solar panels: 'Has the potential to contribute to the energy transition'
-
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/24690127
Solar energy experts in Germany are putting sun-catching cells under the magnifying glass with astounding results, according to multiple reports.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems team is perfecting the use of lenses to concentrate sunlight onto solar panels, reducing size and costs while increasing performance, Interesting Engineering and PV Magazine reported.
The "technology has the potential to contribute to the energy transition, facilitating the shift toward more sustainable and renewable energy sources by combining minimal carbon footprint and energy demand with low levelized cost of electricity," the researchers wrote in a study published by the IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics.
The sun-catcher is called a micro-concentrating photovoltaic, or CPV, cell. The lens makes it different from standard solar panels that convert sunlight to energy with average efficiency rates around 20%, per MarketWatch. Fraunhofer's improved CPV cell has an astounding 36% rate in ideal conditions and is made with lower-cost parts. It cuts semiconductor materials "by a factor of 1,300 and reduces module areas by 30% compared to current state-of-the-art CPV systems," per IE.
-
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/24690127
Solar energy experts in Germany are putting sun-catching cells under the magnifying glass with astounding results, according to multiple reports.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems team is perfecting the use of lenses to concentrate sunlight onto solar panels, reducing size and costs while increasing performance, Interesting Engineering and PV Magazine reported.
The "technology has the potential to contribute to the energy transition, facilitating the shift toward more sustainable and renewable energy sources by combining minimal carbon footprint and energy demand with low levelized cost of electricity," the researchers wrote in a study published by the IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics.
The sun-catcher is called a micro-concentrating photovoltaic, or CPV, cell. The lens makes it different from standard solar panels that convert sunlight to energy with average efficiency rates around 20%, per MarketWatch. Fraunhofer's improved CPV cell has an astounding 36% rate in ideal conditions and is made with lower-cost parts. It cuts semiconductor materials "by a factor of 1,300 and reduces module areas by 30% compared to current state-of-the-art CPV systems," per IE.
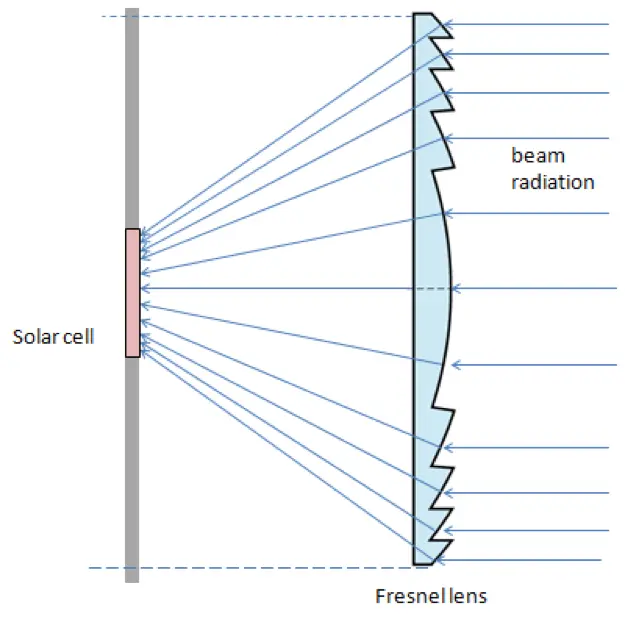
What are concentrating photovoltaics?
One of the ways to increase the output from the photovoltaic systems is to supply concentrated light onto the PV cells. This can be done by using optical light collectors, such as lenses or mirrors. The PV systems that use concentrated light are called concentrating photovoltaics (CPV). The CPV collect light from a larger area and concentrate it to a smaller area solar cell. This is illustrated in Figure 5.1.
Also, from the article - 33.6% efficiency in real-world conditions:
A 60 cell-lens prototype was studied for a year. In "real-world" conditions, CPVs achieved up to 33.6% efficiency. The 36% mark was posted at 167 degrees Fahrenheit. The prototype showed no signs of degradation, according to IE.
-
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/24690127
Solar energy experts in Germany are putting sun-catching cells under the magnifying glass with astounding results, according to multiple reports.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems team is perfecting the use of lenses to concentrate sunlight onto solar panels, reducing size and costs while increasing performance, Interesting Engineering and PV Magazine reported.
The "technology has the potential to contribute to the energy transition, facilitating the shift toward more sustainable and renewable energy sources by combining minimal carbon footprint and energy demand with low levelized cost of electricity," the researchers wrote in a study published by the IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics.
The sun-catcher is called a micro-concentrating photovoltaic, or CPV, cell. The lens makes it different from standard solar panels that convert sunlight to energy with average efficiency rates around 20%, per MarketWatch. Fraunhofer's improved CPV cell has an astounding 36% rate in ideal conditions and is made with lower-cost parts. It cuts semiconductor materials "by a factor of 1,300 and reduces module areas by 30% compared to current state-of-the-art CPV systems," per IE.
is it a real thing or an obligatory overestimated result to get grants because the system is fucked?
-
What are concentrating photovoltaics?
One of the ways to increase the output from the photovoltaic systems is to supply concentrated light onto the PV cells. This can be done by using optical light collectors, such as lenses or mirrors. The PV systems that use concentrated light are called concentrating photovoltaics (CPV). The CPV collect light from a larger area and concentrate it to a smaller area solar cell. This is illustrated in Figure 5.1.

Also, from the article - 33.6% efficiency in real-world conditions:
A 60 cell-lens prototype was studied for a year. In "real-world" conditions, CPVs achieved up to 33.6% efficiency. The 36% mark was posted at 167 degrees Fahrenheit. The prototype showed no signs of degradation, according to IE.
A lighthouse uses the same lens, just with the light coming from the inside. Since this is old knowledge, what is the drawback? Why isn't this widespread?
My completely uninformed guess:
-
The lens and assembly costs too much compared to just more solar panels
-
The lens/panel combo is so bulky/prone to failure it becomes unreasonable to actually install/use.
-
-
A lighthouse uses the same lens, just with the light coming from the inside. Since this is old knowledge, what is the drawback? Why isn't this widespread?
My completely uninformed guess:
-
The lens and assembly costs too much compared to just more solar panels
-
The lens/panel combo is so bulky/prone to failure it becomes unreasonable to actually install/use.
The article states that it’s smaller and cheaper. The reason it’s not widespread is that they just invented it.
-
-
is it a real thing or an obligatory overestimated result to get grants because the system is fucked?
I just skimmed the IEEE paper (peer-reviewed, solid journal); The usage of 'slash costs' in the title is entire sensational. The tech gave a SLIGHT increase in efficiency (which is good news - marginal improvements are still very good and can be game-changing if scaled up), but there is no cost/benefit analysis in the paper regarding the additional costs of lenses and whether the increased PV efficiency would offset those costs at scale.
-
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/24690127
Solar energy experts in Germany are putting sun-catching cells under the magnifying glass with astounding results, according to multiple reports.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems team is perfecting the use of lenses to concentrate sunlight onto solar panels, reducing size and costs while increasing performance, Interesting Engineering and PV Magazine reported.
The "technology has the potential to contribute to the energy transition, facilitating the shift toward more sustainable and renewable energy sources by combining minimal carbon footprint and energy demand with low levelized cost of electricity," the researchers wrote in a study published by the IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics.
The sun-catcher is called a micro-concentrating photovoltaic, or CPV, cell. The lens makes it different from standard solar panels that convert sunlight to energy with average efficiency rates around 20%, per MarketWatch. Fraunhofer's improved CPV cell has an astounding 36% rate in ideal conditions and is made with lower-cost parts. It cuts semiconductor materials "by a factor of 1,300 and reduces module areas by 30% compared to current state-of-the-art CPV systems," per IE.
Wouldn't this be negated by the fact, that the same area of roof now has less actual PV cell on it? Since the light gets concentrated on a smaller area?
-
A lighthouse uses the same lens, just with the light coming from the inside. Since this is old knowledge, what is the drawback? Why isn't this widespread?
My completely uninformed guess:
-
The lens and assembly costs too much compared to just more solar panels
-
The lens/panel combo is so bulky/prone to failure it becomes unreasonable to actually install/use.
Adding to what Eldest_Malk said: They aren't just putting a new type of lens over standard solar cells, they are also designing/fabricating custom cells to work with the lenses. [I'm not a PV expert, but the fact that the IEEE paper focuses so much on the cells and not just the lenses leads me to believe that the lenses can't just be used with whatever standardized solar cells are on the market]
-
-
A lighthouse uses the same lens, just with the light coming from the inside. Since this is old knowledge, what is the drawback? Why isn't this widespread?
My completely uninformed guess:
-
The lens and assembly costs too much compared to just more solar panels
-
The lens/panel combo is so bulky/prone to failure it becomes unreasonable to actually install/use.
They mention standardisations and cost savings in their paper, as well as solving the heat load per cell problem by decreasing cell size. They also mention that there's been a lot of micro-CPV module designs but that they haven't been scaled up. Some quotes below:
Various researchers and developers have been exploring different micro-CPV module designs [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13]. Most approaches have been tested on small prototypes or minimodules, while fewer have been realized with aperture areas (Aap) above 200 and 800 cm2,[...]
By decreasing the sizes of the primary optics and the solar cells, the heat load per cell is minimized. This reduction allows for sufficient heat spreading via the circuit board, enabling the direct assembly of solar cells onto the circuit board on glass.
At Fraunhofer ISE, we have developed a micro-CPV module concept [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], which is based on parallelized manufacturing processes and commercially available components.
The final module features a panel size of 24” × 18”, which is a standard in the microelectronics industry, facilitating machine adaption without necessitating special adjustments.
-
-
Wouldn't this be negated by the fact, that the same area of roof now has less actual PV cell on it? Since the light gets concentrated on a smaller area?
I think the idea is that it’s the same amount of light is being used but the actual expensive part of the solar cell is cheaper and designed to take the increased heat. So the same size “solar unit” on the roof collecting the same amount of light and generating the same amount of energy but cheaper overall. At least that was my take. Correct me if I’m wrong.
-
Wouldn't this be negated by the fact, that the same area of roof now has less actual PV cell on it? Since the light gets concentrated on a smaller area?
I think the point is that you can replace one big solar panel with one big lens and a small solar panel. The footprint on the roof is the same, but the implication is a big glass lens is cheaper than a big solar panel.
-
The article states that it’s smaller and cheaper. The reason it’s not widespread is that they just invented it.
It is interesting that someone just recently thought to use a fresnel lens with photovoltaics when they’ve existed for hundreds of years
-
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/24690127
Solar energy experts in Germany are putting sun-catching cells under the magnifying glass with astounding results, according to multiple reports.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems team is perfecting the use of lenses to concentrate sunlight onto solar panels, reducing size and costs while increasing performance, Interesting Engineering and PV Magazine reported.
The "technology has the potential to contribute to the energy transition, facilitating the shift toward more sustainable and renewable energy sources by combining minimal carbon footprint and energy demand with low levelized cost of electricity," the researchers wrote in a study published by the IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics.
The sun-catcher is called a micro-concentrating photovoltaic, or CPV, cell. The lens makes it different from standard solar panels that convert sunlight to energy with average efficiency rates around 20%, per MarketWatch. Fraunhofer's improved CPV cell has an astounding 36% rate in ideal conditions and is made with lower-cost parts. It cuts semiconductor materials "by a factor of 1,300 and reduces module areas by 30% compared to current state-of-the-art CPV systems," per IE.
I am not a scientist so please correct me if I am off base, but did it really take them this long to attempt to focus light onto PV cells using a fresnel lens?
My hobby as a 15 year old was buying broken projectors to harvest the fresnel lenses in the lamp on top. They could focus sunlight so powerfully that you could burn shit. I didn't do that, surprisingly. I was like Marge Simpson, I just thought they were neat.
-
It is interesting that someone just recently thought to use a fresnel lens with photovoltaics when they’ve existed for hundreds of years
This is exactely how most inventions are made: put together two things from different realms that might have a good fit.
Just wait a few years and they will find a way to use the light directly instead transferring it into electricity. There‘re some IC‘s that already use light instead of voltage to compute.
-
I just skimmed the IEEE paper (peer-reviewed, solid journal); The usage of 'slash costs' in the title is entire sensational. The tech gave a SLIGHT increase in efficiency (which is good news - marginal improvements are still very good and can be game-changing if scaled up), but there is no cost/benefit analysis in the paper regarding the additional costs of lenses and whether the increased PV efficiency would offset those costs at scale.
Honestly, we don't need the technology to get any better than it is. It's nice, but not necessary. Labor costs of deployment are the biggest limiting factor.
-
It is interesting that someone just recently thought to use a fresnel lens with photovoltaics when they’ve existed for hundreds of years
It isn't that. They have been talking about Fresnel lenses on PV for decades. It's solving the heat issue and the size issue. A Fresnel lens gathers a large area of light and focuses it down, including focusing the heat. Normal PV cells cannot handle that amount of heat.
-
I am not a scientist so please correct me if I am off base, but did it really take them this long to attempt to focus light onto PV cells using a fresnel lens?
My hobby as a 15 year old was buying broken projectors to harvest the fresnel lenses in the lamp on top. They could focus sunlight so powerfully that you could burn shit. I didn't do that, surprisingly. I was like Marge Simpson, I just thought they were neat.
IIRC, this sort of thing has been floated before. The issue is that you can't just focus that much light on the solar cell. It'll burn out.
-
I am not a scientist so please correct me if I am off base, but did it really take them this long to attempt to focus light onto PV cells using a fresnel lens?
My hobby as a 15 year old was buying broken projectors to harvest the fresnel lenses in the lamp on top. They could focus sunlight so powerfully that you could burn shit. I didn't do that, surprisingly. I was like Marge Simpson, I just thought they were neat.
OK, take that Fresnel lens that you were using to melt pennies and then focus it on a PV cell that is also made of metal. What might be the expected response? The science in this case is making PV cells that can handle the intense heat.
-
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/24690127
Solar energy experts in Germany are putting sun-catching cells under the magnifying glass with astounding results, according to multiple reports.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems team is perfecting the use of lenses to concentrate sunlight onto solar panels, reducing size and costs while increasing performance, Interesting Engineering and PV Magazine reported.
The "technology has the potential to contribute to the energy transition, facilitating the shift toward more sustainable and renewable energy sources by combining minimal carbon footprint and energy demand with low levelized cost of electricity," the researchers wrote in a study published by the IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics.
The sun-catcher is called a micro-concentrating photovoltaic, or CPV, cell. The lens makes it different from standard solar panels that convert sunlight to energy with average efficiency rates around 20%, per MarketWatch. Fraunhofer's improved CPV cell has an astounding 36% rate in ideal conditions and is made with lower-cost parts. It cuts semiconductor materials "by a factor of 1,300 and reduces module areas by 30% compared to current state-of-the-art CPV systems," per IE.
How does concentrating the sunlight like this not start a fire? Or wouldn’t this at least cause panel electronics to overheat?
-
I am not a scientist so please correct me if I am off base, but did it really take them this long to attempt to focus light onto PV cells using a fresnel lens?
My hobby as a 15 year old was buying broken projectors to harvest the fresnel lenses in the lamp on top. They could focus sunlight so powerfully that you could burn shit. I didn't do that, surprisingly. I was like Marge Simpson, I just thought they were neat.
Not being any kind of solar energy expert, my initial thought was how the cell’s would hold up under the increased heat, and what technology (if any) they’d be using to monitor/mitigate. The article does briefly mention the cells achieving ~33% @ ~167° F, and does mention (what seems to be tangential) technologies that allow for cells to be nailed down as if they were shingles.
My guess is that it isn’t that they finally using techniques that seem obvious to us, but that they’ve developed supporting tech to mitigate the detrimental effects of using magnification.




