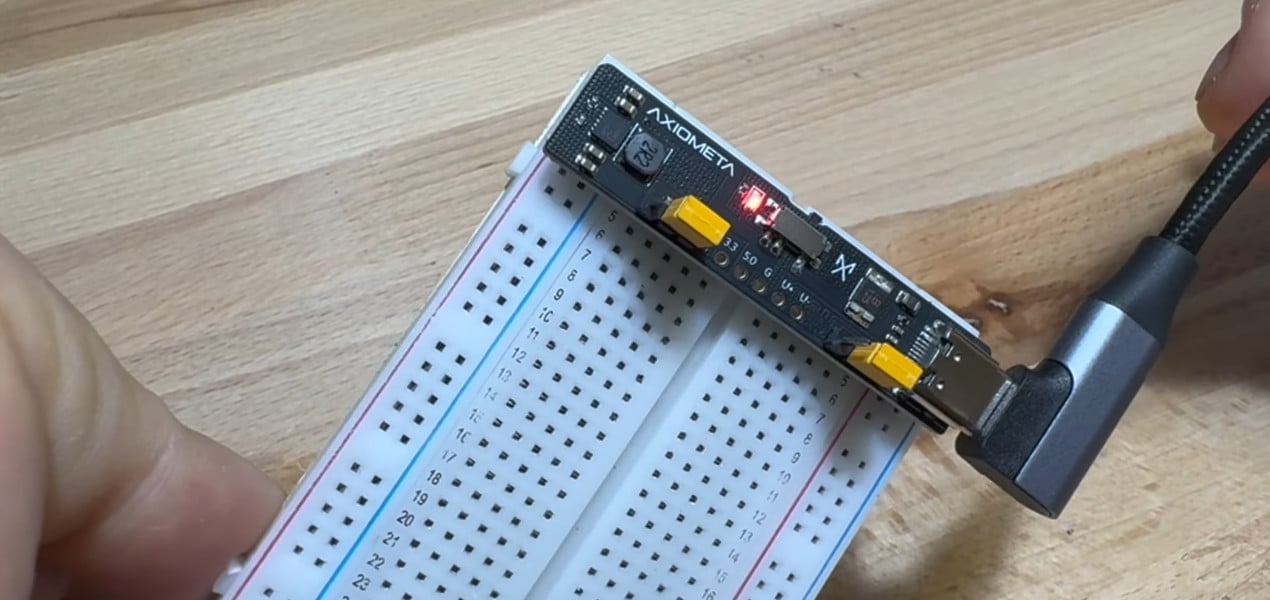
No Frills PCB Brings USB-C Power To The Breadboard
-
This post did not contain any content.
-
This post did not contain any content.
TL;DR - It's a nice and pretty run of the mill breadboard power adaptor which happens to support USB-C connectors, but the article and its title insanely oversell the thing.
--
This is not exact as amazing an achievement as the headline implies since the necessary stuff to talk the to the USB PD host upstream is already integrated so you just need to get a chip that does it (and even without it, you'll get 150mA @ 5V by default out of the USB 3 host upstream and up to 900mA with some pretty basic USB negotiation in a protocol that dates from USB 1.0 and for which there have long been integrated solutions for both the device and the host sides).
Further, the converting of those 5V to 3.3V just requires a buck converter or even just a voltage regulator (though this latter option is less efficient), for which there are already lots of integrated solutions available for peanuts and where the entire circuit block needed to support them is detailed in the datasheet for that converter.
Looking at the circuit diagram for this (linked to from the article), they're not even doing the USB PD negotiation or any kind of USB 1.0 negotiation, so this thing will be limited to 150mA for a USB 3 host or whatever current your traditional USB power source can supply (as those power sources really just do power supply of whatever amperage they support over a cable which happen to have USB connectors, rather than including a genuine implementation of an USB host with current limiting depending on negotiation with the USB device, so such power sources don't require the device to do any USB negotiation to increase the current limit above 150mA).
This is really "yet another run of the mill USB power breadboard adaptor" only the USB plug is USB-C rather than mini-USB or micro-USB (so, a different plug plus a handfull of minor components as per the standard of the circuitry to properly support it), so pretty much the same as the cheap chinese ones you can get from Aliexpress, though this one uses a Buck Converter rather than the $0.1 Voltage Regulator in most of the chinese boards, and actually does proper filtering of power supply noise and proper protection against over current, so it is a quality design for such things, though it's not really a major advancement.
Without the USB PD stuff I wouldn't really say that it brings USB-C Power to the breadboard (in the sense of, as many would expect, being able to draw a proper amount of power from a modern USB 3.0 power brick that supports USB-C), more something with a USB-C connector that brings power to the motherboard, as that connector is really the total sum of what it supports from the modern USB spec.
What would really be nice would be something that does talk USB-PD to the upstream host AND can convert down from the 20V at which it supplies peak power, so that you can take advantage of the juicy, juicy (oh so juicy!) capability of USB-PD to supply power (up to 100W right now, which will be up to 250W with USB 4), though if you're pulling 100W (which at 5V means 20A, which is a stupidly high current that will melt most components in a typical digital circuit) from you breadboard power adaptor, then I'm pretty sure magic smoke is being released from at least one of the components on that breadboard and, by the way, you're probably damaging the power rail of that breadboard (aah, the sweet smell of burnt plastic when you turn the power on for your half-arsed experimental circuit!!!)
-
TL;DR - It's a nice and pretty run of the mill breadboard power adaptor which happens to support USB-C connectors, but the article and its title insanely oversell the thing.
--
This is not exact as amazing an achievement as the headline implies since the necessary stuff to talk the to the USB PD host upstream is already integrated so you just need to get a chip that does it (and even without it, you'll get 150mA @ 5V by default out of the USB 3 host upstream and up to 900mA with some pretty basic USB negotiation in a protocol that dates from USB 1.0 and for which there have long been integrated solutions for both the device and the host sides).
Further, the converting of those 5V to 3.3V just requires a buck converter or even just a voltage regulator (though this latter option is less efficient), for which there are already lots of integrated solutions available for peanuts and where the entire circuit block needed to support them is detailed in the datasheet for that converter.
Looking at the circuit diagram for this (linked to from the article), they're not even doing the USB PD negotiation or any kind of USB 1.0 negotiation, so this thing will be limited to 150mA for a USB 3 host or whatever current your traditional USB power source can supply (as those power sources really just do power supply of whatever amperage they support over a cable which happen to have USB connectors, rather than including a genuine implementation of an USB host with current limiting depending on negotiation with the USB device, so such power sources don't require the device to do any USB negotiation to increase the current limit above 150mA).
This is really "yet another run of the mill USB power breadboard adaptor" only the USB plug is USB-C rather than mini-USB or micro-USB (so, a different plug plus a handfull of minor components as per the standard of the circuitry to properly support it), so pretty much the same as the cheap chinese ones you can get from Aliexpress, though this one uses a Buck Converter rather than the $0.1 Voltage Regulator in most of the chinese boards, and actually does proper filtering of power supply noise and proper protection against over current, so it is a quality design for such things, though it's not really a major advancement.
Without the USB PD stuff I wouldn't really say that it brings USB-C Power to the breadboard (in the sense of, as many would expect, being able to draw a proper amount of power from a modern USB 3.0 power brick that supports USB-C), more something with a USB-C connector that brings power to the motherboard, as that connector is really the total sum of what it supports from the modern USB spec.
What would really be nice would be something that does talk USB-PD to the upstream host AND can convert down from the 20V at which it supplies peak power, so that you can take advantage of the juicy, juicy (oh so juicy!) capability of USB-PD to supply power (up to 100W right now, which will be up to 250W with USB 4), though if you're pulling 100W (which at 5V means 20A, which is a stupidly high current that will melt most components in a typical digital circuit) from you breadboard power adaptor, then I'm pretty sure magic smoke is being released from at least one of the components on that breadboard and, by the way, you're probably damaging the power rail of that breadboard (aah, the sweet smell of burnt plastic when you turn the power on for your half-arsed experimental circuit!!!)
and even without it, you'll get 150mA @ 5V by default out of the USB 3 host upstream and up to 900mA with some pretty basic USB negotiation in a protocol that dates from USB 1.0
That's wrong. With USB Type-C, you can get the power up to 3A @ 5V with just two 5.1kΩ resistor on CC pins.